-
Endpoint Management integration with Microsoft Endpoint Manager
-
Certificates and authentication
-
Client certificate or certificate plus domain authentication
-
Authentication with Azure Active Directory through Citrix Cloud™
-
Authentication with Azure Active Directory Group-Based Administration
-
Authentication with Azure Active Directory through Citrix Gateway for MAM enrollment
-
Authentication with Okta through Citrix Gateway for MAM enrollment
-
Authentication with an on-premises Citrix Gateway through Citrix Cloud
This content has been machine translated dynamically.
Dieser Inhalt ist eine maschinelle Übersetzung, die dynamisch erstellt wurde. (Haftungsausschluss)
Cet article a été traduit automatiquement de manière dynamique. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo lo ha traducido una máquina de forma dinámica. (Aviso legal)
此内容已经过机器动态翻译。 放弃
このコンテンツは動的に機械翻訳されています。免責事項
이 콘텐츠는 동적으로 기계 번역되었습니다. 책임 부인
Este texto foi traduzido automaticamente. (Aviso legal)
Questo contenuto è stato tradotto dinamicamente con traduzione automatica.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
This article has been machine translated.
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. (Haftungsausschluss)
Ce article a été traduit automatiquement. (Clause de non responsabilité)
Este artículo ha sido traducido automáticamente. (Aviso legal)
この記事は機械翻訳されています.免責事項
이 기사는 기계 번역되었습니다.책임 부인
Este artigo foi traduzido automaticamente.(Aviso legal)
这篇文章已经过机器翻译.放弃
Questo articolo è stato tradotto automaticamente.(Esclusione di responsabilità))
Translation failed!
SCEP device policy
This policy lets you configure iOS and macOS devices to retrieve a certificate from an external SCEP server over the Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP). To deliver a certificate to devices using SCEP from a PKI that is connected to Citrix Endpoint Management, create a PKI entity and a PKI provider in distributed mode. For details, see PKI Entities.
To add or configure this policy, go to Configure > Device Policies. For more information, see Device policies.
iOS settings
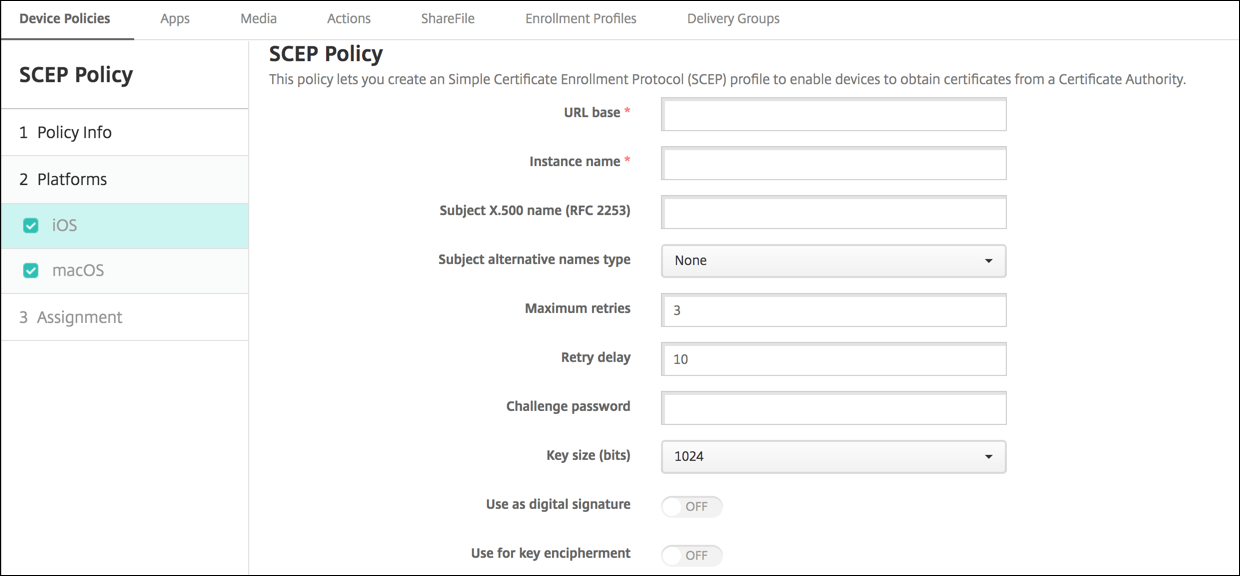
- URL base: Type the address of the SCEP server to define where SCEP requests are sent, over HTTP or HTTPS. The private key isn’t sent with the Certificate Signing Request (CSR), so it might be safe to send the request unencrypted. If the one-time password is configured for reuse, use HTTPS to protect the password. This step is required.
- Instance name: Type any string that the SCEP server recognizes. For example, it can be a domain name like example.org. If a CA has multiple CA certificates, you can use this field to distinguish the required domain. This step is required.
-
Subject X.500 name (RFC 2253): Type the representation of an X.500 name as an array of Object Identifier (OID) and value. For example,
/C=US/O=Apple Inc./CN=foo/1.2.5.3=bar, which translates to:[ [ [“C”, “US”] ], [ [“O”, “Apple Inc.”] ], …, [ [“1.2.5.3”, “bar” ] ] ]. You can represent OIDs as dotted numbers with shortcuts for country (C), locality (L), state (ST), organization (O), organizational unit (OU), and common name (CN). - Subject alternative names type: Select an alternative name type. An optional alternative name type can provide the values required by the CA for issuing a certificate. You can specify None, RFC 822 name, DNS name, or URI.
- Maximum retries: Type the number of times a device must retry when the SCEP server sends a PENDING response. The default is 3.
- Retry delay: Type the number of seconds to wait between subsequent retries. The first retry is attempted without delay. The default is 10.
- Challenge password: Enter a pre-shared secret.
- Key size (bits): Select 2048 or higher as the key size in bits.
- Use as digital signature: Choose whether to use the certificate as a digital signature. The SCEP server verifies the certificate use as a digital signature before using the public key to decrypt the hash.
- Use for key encipherment: Choose whether to use the certificate for key encipherment. A server first checks whether the certificate provided by a client is allowed for key encipherment. Then the server uses the public key in a certificate to verify that a piece of data was encrypted using the private key. If not, the operation fails.
-
SHA-256 fingerprint (hexadecimal string): If your CA uses HTTP, use this field to provide the fingerprint of the CA certificate. The device uses the fingerprint to confirm the authenticity of the CA response during enrollment. You can provide an SHA-256 fingerprint, or you can select a certificate to import its signature.
-
Policy settings
-
Remove policy: Choose a method for scheduling policy removal. Available options are Select date and Duration until removal (in hours)
- Select date: Click the calendar to select the specific date for removal.
- Duration until removal (in hours): Type a number, in hours, until policy removal occurs. Only available for iOS 6.0 and later.
-
Remove policy: Choose a method for scheduling policy removal. Available options are Select date and Duration until removal (in hours)
macOS settings
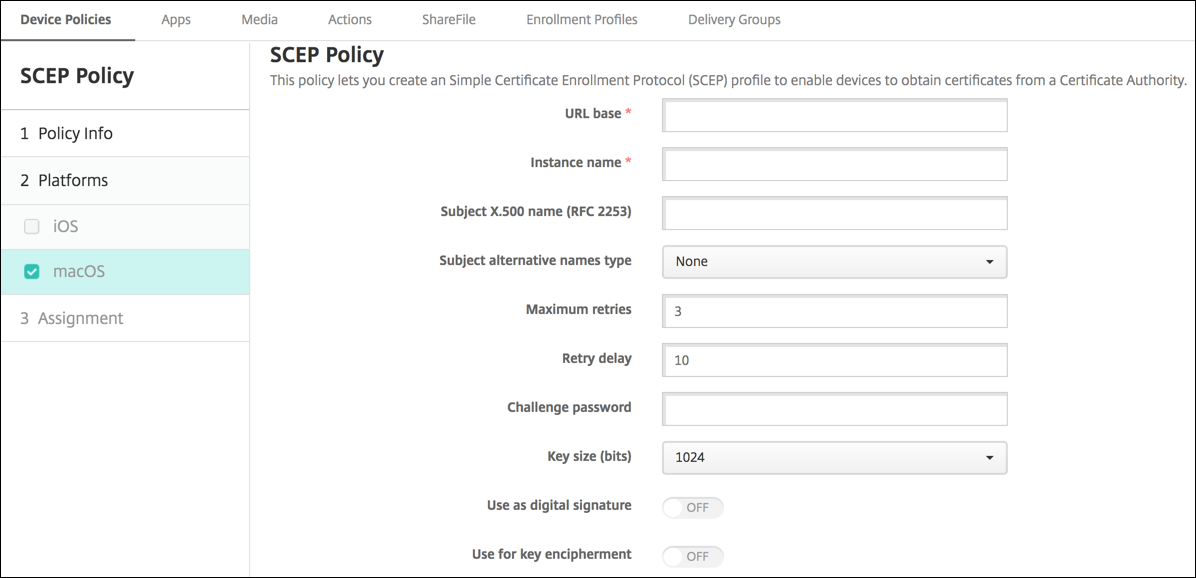
- URL base: Type the address of the SCEP server to define where SCEP requests are sent, over HTTP or HTTPS. The private key isn’t sent with the Certificate Signing Request (CSR), so it might be safe to send the request unencrypted. If the one-time password is configured for reuse, use HTTPS to protect the password. This step is required.
- Instance name: Type any string that the SCEP server recognizes. For example, it can be a domain name like example.org. If a CA has multiple CA certificates, you can use this field to distinguish the required domain. This step is required.
-
Subject X.500 name (RFC 2253): Type the representation of an X.500 name as an array of Object Identifier (OID) and value. For example,
/C=US/O=Apple Inc./CN=foo/1.2.5.3=bar, which translates to:[ [ [“C”, “US”] ], [ [“O”, “Apple Inc.”] ], …, [ [“1.2.5.3”, “bar” ] ] ]. You can represent OIDs as dotted numbers with shortcuts for country (C), locality (L), state (ST), organization (O), organizational unit (OU), and common name (CN). - Subject alternative names type: Select an alternative name type. An optional alternative name type can provide the values required by the CA for issuing a certificate. You can specify None, RFC 822 name, DNS name, or URI.
- Maximum retries: Type the number of times a device must retry when the SCEP server sends a PENDING response. The default is 3.
- Retry delay: Type the number of seconds to wait between subsequent retries. The first retry is attempted without delay. The default is 10.
- Challenge password: Type a pre-shared secret.
- Key size (bits): Select 2048 or higher as the key size in bits.
- Use as digital signature: Choose whether to use the certificate as a digital signature. The SCEP server verifies the certificate use as a digital signature before using the public key to decrypt the hash.
- Use for key encipherment: Choose whether to use the certificate for key encipherment. A server first checks whether the certificate provided by a client is allowed for key encipherment. Then the server uses the public key in a certificate to verify that a piece of data was encrypted using the private key. If not, the operation fails.
-
SHA-256 fingerprint (hexadecimal string): If your CA uses HTTP, use this field to provide the fingerprint of the CA certificate. The device uses the fingerprint to confirm the authenticity of the CA response during enrollment. You can provide an SHA-256 fingerprint, or you can select a certificate to import its signature.
-
Policy settings
-
Remove policy: Choose a method for scheduling policy removal. Available options are Select date and Duration until removal (in hours)
- Select date: Click the calendar to select the specific date for removal.
- Duration until removal (in hours): Type a number, in hours, until policy removal occurs.
- Allow user to remove policy: You can select when users can remove the policy from their device. Select Always, Passcode required, or Never from the menu. If you select Passcode required, type a passcode in the Removal passcode field.
- Profile scope: Select whether this policy applies to a User or an entire System. The default is User. This option is available only on macOS 10.7 and later.
-
Remove policy: Choose a method for scheduling policy removal. Available options are Select date and Duration until removal (in hours)
Share
Share
In this article
This Preview product documentation is Citrix Confidential.
You agree to hold this documentation confidential pursuant to the terms of your Citrix Beta/Tech Preview Agreement.
The development, release and timing of any features or functionality described in the Preview documentation remains at our sole discretion and are subject to change without notice or consultation.
The documentation is for informational purposes only and is not a commitment, promise or legal obligation to deliver any material, code or functionality and should not be relied upon in making Citrix product purchase decisions.
If you do not agree, select I DO NOT AGREE to exit.