Tools and utilities
Session data query utility
We provide a utility (ctxsdcutil) that you can use to query session data on each Linux VDA. To query the following data of all sessions or a specific session hosted on a VDA, run the /opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/ctxsdcutil -q <all | SessionID> [-c] command. The [-c] argument means to query data every second.
-
Input Session Bandwidth
-
Output Session Bandwidth
-
Output Session Line Speed
-
Latency - Last Recorded
-
Round Trip Time
-
Output ThinWire Bandwidth
-
Output Audio Bandwidth
-
Output Printer Bandwidth
-
Input Drive Bandwidth
-
Output Drive Bandwidth
The xdlcollect Bash script
The xdlcollect Bash script used to collect logs is integrated into the Linux VDA software and located under /opt/Citrix/VDA/bin. After you install the Linux VDA, you can run the bash /opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/xdlcollect.sh command to collect logs. After the log collection completes, a compressed log file is generated in the same folder as the script. The xdlcollect Bash script can ask you whether to upload the compressed log file to Citrix Insight Services (CIS). If you agree, xdlcollect returns an upload_ID after the upload completes. The upload does not remove the compressed log file from your local machine. Other users can use the upload_ID to access the log file in CIS.
XDPing
The Linux XDPing tool is a command-line application. It automates the process of checking for common configuration issues with a Linux VDA environment.
Install the Linux XDPing tool
Running ctxsetup.sh does not install XDPing. To install XDPing, run sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/xdping.
This command also creates a Python3 virtual environment that is required for XDPing. If this command fails to create a Python3 virtual environment, create it manually following the instructions at Create a Python3 virtual environment.
To address SSL connection errors that you might encounter when using the pip tool, consider adding the following trusted hosts to the /etc/pip.conf file:
[global]
trusted-host =
pypi.org
files.pythonhosted.org
Tasks that can be done with XDPing
XDPing comes with the single executable named xdping that is run from the command shell.
The following table describes the various tasks that can be done with the corresponding XDPing commands:
| Task | XDPing Command | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| To display the command-line options | sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/xdping -h | N/A |
| To run the full suite of tests | sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/xdping (run XDPing without any command-line option) | The Linux XDPing tool performs over 150 individual tests on the system. For more information, see Individual tests later in this article. |
| To run a VDA registration status check | sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/xdping -a | For more information, see Scope of registration status checks later in this article. |
| To back up the key data of a VDA | sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/xdping -b | For more information, see Backup and comparison of VDA data later in this article. |
| To compare the latest two copies of VDA backup data | sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/xdping -diff | For more information, see Backup and comparison of VDA data later in this article. |
| To compare two specific copies of VDA backup data | **sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/xdping -diff= |
For more information, see Backup and comparison of VDA data later in this article. |
| To check the environment before installing the Linux VDA package | sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/xdping –preflight | N/A |
| To run specific test categories only, for example, the time, Kerberos, and database tests | sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/xdping -T time,kerberos,database | N/A |
| To probe a particular Delivery Controller | **sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/xdping -d |
N/A |
Individual tests
The Linux XDPing tool performs over 150 individual tests on the system, which are broadly categorized as follows:
- Check whether Linux VDA system requirements are met.
- Identify and display machine information including the Linux distributions.
- Check the Linux kernel compatibility.
- Check for any known Linux distribution issues that can impact the Linux VDA operation.
- Check the Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux) mode and compatibility.
- Identify network interfaces and check network settings.
- Check storage partitioning and available disk space.
- Check machine host and domain name configuration.
- Check DNS configuration and perform lookup tests.
- Identify underlying hypervisors and check virtual machine configuration. Support for:
- Citrix Hypervisor™
- Microsoft HyperV
- VMware vSphere
- Check time settings and check whether network time synchronization is operational.
- Check whether the PostgreSQL service is properly configured and operational.
- Check whether SQLite is properly configured and operational.
- Check whether the firewall is enabled and the required ports are open.
- Check Kerberos configuration and perform authentication tests.
- Check the LDAP search environment for the group policy service engine.
- Check whether Active Directory integration is set up properly and the current machine is joined to the domain. Support for:
- Samba Winbind
- Dell Quest Authentication Services
- Centrify DirectControl
- SSSD
- Check the integrity of the Linux computer object in the Active Directory.
- Check Pluggable Authentication Module (PAM) configuration.
- Check the core dump pattern.
- Check whether packages required by the Linux VDA are installed.
- Identify the Linux VDA package and check the integrity of the installation.
- Check the integrity of the PostgreSQL registry database.
- Check whether the Linux VDA services are properly configured and operational.
- Check the integrity of the VDA and HDX™ configuration.
- Probe each configured Delivery Controller™ to test that the Broker Service is reachable, operational, and responsive.
- Check whether the machine is registered with the Delivery Controller farm.
- Check the state of each active or disconnected HDX session.
- Scan log files for the Linux VDA related errors and warnings.
- Check whether the version of Xorg is suitable.
- Check whether required dependencies are installed.
Sample output
The following is a sample output from running the Kerberos test:
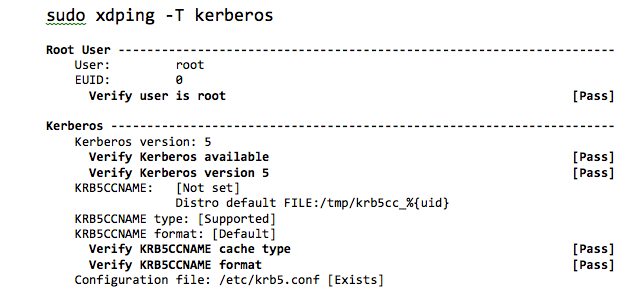
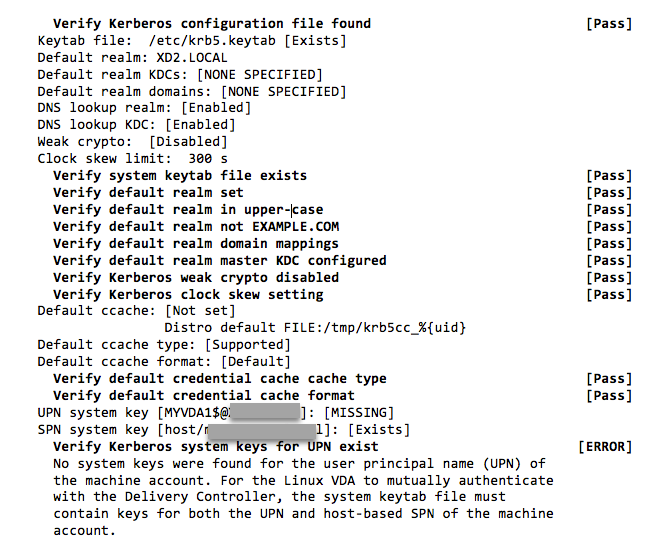

Scope of VDA registration status checks
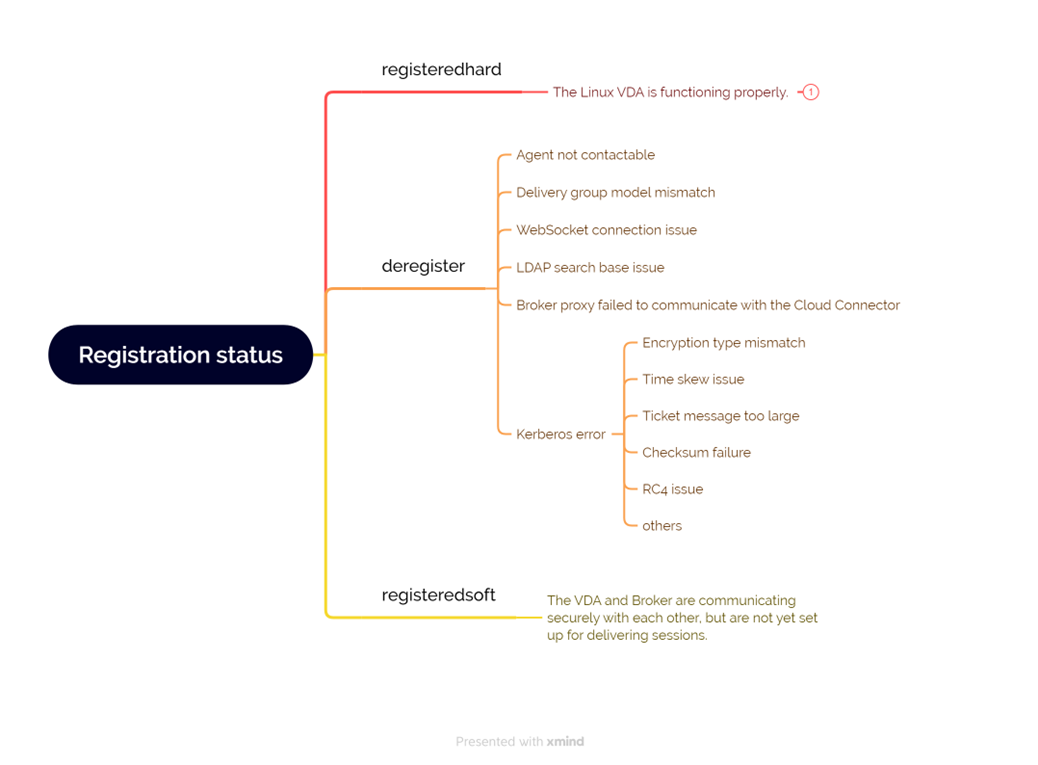
The Linux XDPing tool also provides an analysis module to help you check and analyze your VDA registration status. For a scope of registration status checks, see the following screen capture:
Backup and comparison of VDA data
Starting with the Linux VDA 2305, the XDPing tool introduces a VDA backup module. This module lets you back up the key data of a VDA at any time, such as the configuration, database, and binary permission data. You can back up the key data of a VDA when it is running properly. In case the VDA fails later, back up another copy of the data and compare the two copies of data to facilitate troubleshooting. The following table describes VDA data backup and comparison with the corresponding XDPing commands:
| Task | XDPing Command | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| To back up the key data of a VDA | sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/xdping -b | Each time you run the backup command, a copy of the backup data is generated and saved in a directory under /var/ctxbackup. The backup data directories are named the current date and time in yyyy-mm-dd-hh_mm_ss format, for example, 2023-02-27-16_31_27. By default, the maximum number of backup data directories is 30 and the XDPing tool rotates or deletes old backup data directories when the number is exceeded. To customize the number for directory rotation, run the following command: sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/ctxreg create -k "HKLM\Software\Citrix\VirtualDesktopAgent\Backup" -t "REG_DWORD" -v "MaxDirRotationCount" -d "0x0000005" --force
|
| To compare the latest two copies of VDA backup data | sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/xdping -diff | N/A |
| To compare two specific copies of VDA backup data | **sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/xdping -diff= |
N/A |