Quick installation by using easy install (Recommended)
Important:
For fresh installations, we recommend you refer to this article for a quick installation. This article steps through how to install and configure the Linux VDA by using easy install. Easy install saves time and labor and is less error-prone than manual installation. It helps you set up a running environment of the Linux VDA by installing the necessary packages and customizing the configuration files automatically.
To create non-domain joined VDAs, you must use Machine Creation Services (MCS). For more information, see Use Machine Creation Services (MCS) to create Linux VMs.
To learn about features available for non-domain-joined VDAs, go to Non-domain-joined VDAs.
Step 1: Prepare configuration information and the Linux machine
Collect the following configuration information needed for easy install:
- Host name - Host name of the machine on which the Linux VDA is to be installed
- IP address of Domain Name Server
- IP address or string name of NTP Server
- Domain name - The NetBIOS name of the domain
- Realm name - The Kerberos realm name
- Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the domain
Important:
- To install the Linux VDA, verify that the repositories are added correctly on the Linux machine.
- To launch a session, verify that the X Window system and desktop environments are installed.
Considerations
-
The workgroup name, by default, is the domain name. To customize the workgroup in your environment, do the following:
a. Create the /tmp/ctxinstall.conf file on the Linux VDA machine.
b. Add the workgroup=<your workgroup> line to the file and save your changes. -
Centrify does not support pure IPv6 DNS configuration. At least one DNS server using IPv4 is required in /etc/resolv.conf for
adclientto find AD services properly.Log:
ADSITE : Check that this machine's subnet is in a site known by AD : Failed : This machine's subnet is not known by AD. : We guess you should be in the site Site1. <!--NeedCopy-->This issue is unique to Centrify and its configuration. To resolve this issue, do the following:
a. Open Administrative Tools on the domain controller.
b. Select Active Directory Sites and Services.
c. Add a proper subnet address for Subnets. -
To join your VDA to a specific OU, do the following:
-
Ensure that the specific OU exists on the domain controller.
For an example OU, see the following screen capture
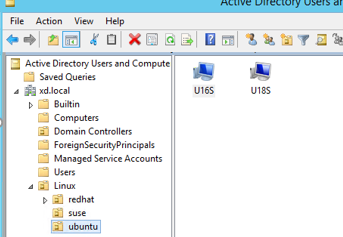
- Create the /tmp/ctxinstall.conf file on the VDA.
-
Add the ou=<your ou> line to the /tmp/ctxinstall.conf file.
OU values vary with different AD methods. See the following table.
OS Winbind SSSD Centrify PBIS Amazon Linux 2 ou="Linux/amazon"ou="Linux/amazon"ou="XD.LOCAL/Linux/amazon"ou="Linux/amazon"Debian ou="Linux/debian"ou="Linux/debian"ou="XD.LOCAL/Linux/debian"ou="Linux/debian"RHEL 8, Rocky Linux 8 ou="OU=redhat,OU=Linux"ou="OU=redhat,OU=Linux"ou="XD.LOCAL/Linux/redhat"ou="Linux/redhat"RHEL 7 ou="Linux/redhat"ou="Linux/redhat"ou="XD.LOCAL/Linux/redhat"ou="Linux/redhat"SUSE ou="Linux/suse"ou="Linux/suse"ou="XD.LOCAL/Linux/suse"ou="Linux/suse"Ubuntu ou="Linux/ubuntu"ou="Linux/ubuntu"ou="XD.LOCAL/Linux/ubuntu"ou="Linux/ubuntu"
-
-
Easy install supports pure IPv6 starting from the Linux VDA 7.16. The following preconditions and limitations apply:
- Your Linux repository must be configured to ensure that your machine can download the required packages over pure IPv6 networks.
- Centrify is not supported on pure IPv6 networks.
Note:
If your network is pure IPv6 and all your input is in proper IPv6 format, the VDA registers with the Delivery Controller™ through IPv6. If your network has a hybrid IPv4 and IPv6 configuration, the type of the first DNS IP address determines whether IPv4 or IPv6 is used for registration.
-
If you choose Centrify as the method to join a domain, the ctxinstall.sh script requires the Centrify package. There are two ways for ctxinstall.sh to get the Centrify package:
-
Easy install helps download the Centrify package from the Internet automatically. The following are the URLs for each distribution:
-
Fetch the Centrify package from a local directory. To designate the directory of the Centrify package, do the following:
a. Create the /tmp/ctxinstall.conf file on the Linux VDA server if it does not exist.
b. Add the “centrifypkgpath=<path name>” line to the file.For example:
cat /tmp/ctxinstall.conf set "centrifypkgpath=/home/mydir" ls -ls /home/mydir 9548 -r-xr-xr-x. 1 root root 9776688 May 13 2016 adcheck-rhel4-x86_64 4140 -r--r--r--. 1 root root 4236714 Apr 21 2016 centrifyda-3.3.1-rhel4-x86_64.rpm 33492 -r--r--r--. 1 root root 34292673 May 13 2016 centrifydc-5.3.1-rhel4-x86_64.rpm 4 -rw-rw-r--. 1 root root 1168 Dec 1 2015 centrifydc-install.cfg 756 -r--r--r--. 1 root root 770991 May 13 2016 centrifydc-ldapproxy-5.3.1-rhel4-x86_64.rpm 268 -r--r--r--. 1 root root 271296 May 13 2016 centrifydc-nis-5.3.1-rhel4-x86_64.rpm 1888 -r--r--r--. 1 root root 1930084 Apr 12 2016 centrifydc-openssh-7.2p2-5.3.1-rhel4-x86_64.rpm 124 -rw-rw-r--. 1 root root 124543 Apr 19 2016 centrify-suite.cfg 0 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 10 Jul 9 2012 install-express.sh -> install.sh 332 -r-xr-xr--. 1 root root 338292 Apr 10 2016 install.sh 12 -r--r--r--. 1 root root 11166 Apr 9 2015 release-notes-agent-rhel4-x86_64.txt 4 -r--r--r--. 1 root root 3732 Aug 24 2015 release-notes-da-rhel4-x86_64.txt 4 -r--r--r--. 1 root root 2749 Apr 7 2015 release-notes-nis-rhel4-x86_64.txt 12 -r--r--r--. 1 root root 9133 Mar 21 2016 release-notes-openssh-rhel4-x86_64.txt <!--NeedCopy-->
-
-
If you choose PBIS as the method to join a domain, the ctxinstall.sh script requires the PBIS package. There are two ways for ctxinstall.sh to get the PBIS package:
-
Easy install helps download the PBIS package from the Internet automatically. For example, the following are the URLs for each distribution:
Amazon Linux 2, CentOS 7, RHEL 8, RHEL 7, SUSE 15.3:
wget https://github.com/BeyondTrust/pbis-open/releases/download/9.1.0/pbis-open-9.1.0.551.linux.x86_64.rpm.shDebian, Ubuntu:
wget https://github.com/BeyondTrust/pbis-open/releases/download/9.1.0/pbis-open-9.1.0.551.linux.x86_64.deb.sh -
Fetch a specific version of the PBIS package from the Internet. To do so, change the “pbisDownloadRelease” and “pbisDownloadExpectedSHA256” lines in the /opt/Citrix/VDA/sbin/ctxinstall.sh file.
For an example, see the following screen capture:
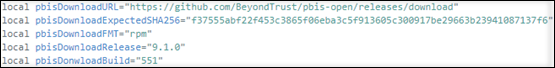
-
Step 2: Prepare the hypervisor
Some changes are required when running the Linux VDA as a virtual machine on a supported hypervisor. Make the following changes based on the hypervisor platform in use. No changes are required if you are running the Linux machine on bare metal hardware.
Fix time synchronization on Citrix Hypervisor™
When the Citrix Hypervisor Time Sync feature is enabled, within each paravirtualized Linux VM you experience issues with NTP and Citrix Hypervisor. Both try to manage the system clock. To avoid the clock becoming out of sync with other servers, make sure that the system clock within each Linux guest is synchronized with the NTP. This case requires disabling host time synchronization. No changes are required in HVM mode.
If you are running a paravirtualized Linux kernel with Citrix VM Tools installed, you can check whether the Citrix Hypervisor Time Sync feature is present and enabled from within the Linux VM:
su -
cat /proc/sys/xen/independent_wallclock
<!--NeedCopy-->
This command returns 0 or 1:
- 0 - The time sync feature is enabled, and must be disabled.
- 1 - The time sync feature is disabled, and no further action is required.
If the /proc/sys/xen/independent_wallclock file is not present, the following steps are not required.
If enabled, disable the time sync feature by writing 1 to the file:
sudo echo 1 > /proc/sys/xen/independent_wallclock
<!--NeedCopy-->
To make this change permanent and persistent after restart, edit the /etc/sysctl.conf file and add the line:
xen.independent_wallclock = 1
To verify these changes, restart the system:
su -
cat /proc/sys/xen/independent_wallclock
<!--NeedCopy-->
This command returns the value 1.
Fix time synchronization on Microsoft Hyper-V
The Linux VMs with Hyper-V Linux Integration Services installed can apply the Hyper-V time synchronization feature to use the time of the host operating system. To ensure that the system clock remains accurate, you must enable this feature alongside the NTP services.
From the management operating system:
- Open the Hyper-V Manager console.
- For the settings of a Linux VM, select Integration Services.
- Ensure that Time synchronization is selected.
Note:
This approach is different from VMware and Citrix Hypervisor, where host time synchronization is disabled to avoid conflicts with NTP. Hyper-V time synchronization can coexist and supplement NTP time synchronization.
Fix time synchronization on ESX and ESXi
When the VMware Time Synchronization feature is enabled, within each paravirtualized Linux VM you experience issues with the NTP and the hypervisor. Both try to synchronize the system clock. To avoid the clock becoming out of sync with other servers, ensure that the system clock within each Linux guest is synchronized with the NTP. This case requires disabling host time synchronization.
If you are running a paravirtualized Linux kernel with VMware Tools installed:
- Open the vSphere Client.
- Edit settings for the Linux VM.
- In the Virtual Machine Properties dialog, open the Options tab.
- Select VMware Tools.
- In the Advanced box, clear Synchronize guest time with host.
Step 3: Install .NET Runtime 6.0 as a prerequisite
Before installing the Linux VDA, install .NET Runtime 6.0 according to the instructions at https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/core/install/linux-package-managers.
After installing .NET Runtime 6.0, run the which dotnet command to find your runtime path.
Based on the command output, set the .NET runtime binary path. For example, if the command output is /aa/bb/dotnet, use /aa/bb as the .NET binary path.
Step 4: Download the Linux VDA package
- Go to the Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops download page.
- Expand the appropriate version of Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops.
-
Click Components to download the Linux VDA package that matches your Linux distribution and the GPG public key that you can use to verify the integrity of the Linux VDA package.
To verify the integrity of the Linux VDA package by using the public key:
-
For an RPM package, import the public key into the RPM database and run the following commands:
rpmkeys --import <path to the public key> rpm --checksig --verbose <path to the Linux VDA package> <!--NeedCopy--> -
For a DEB package, import the public key into the DEB database and run the following commands:
sudo apt-get install dpkg-sig gpg --import <path to the public key> dpkg-sig --verify <path to the Linux VDA package> <!--NeedCopy-->
-
Step 5: Install the Linux VDA package
To set up the environment for the Linux VDA, run the following commands.
For RHEL, CentOS, and Rocky Linux distributions:
sudo yum -y localinstall <PATH>/<Linux VDA RPM>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Note:
For RHEL and CentOS, install the EPEL repository before you can install the Linux VDA successfully. For information on how to install EPEL, see the instructions at https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/epel/.
For Ubuntu/Debian distributions:
sudo dpkg -i <PATH>/<Linux VDA deb>
sudo apt-get install -f
<!--NeedCopy-->
Note:
- To install the necessary dependencies for a Debian 11.3 distribution, add the
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian/ bullseye mainline to the /etc/apt/sources.list file.- To install the necessary dependencies for a Debian 10.9 distribution, add the
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian/ oldstable mainline to the /etc/apt/sources.list file.
For SUSE distributions:
zypper -i install <PATH>/<Linux VDA RPM>
<!--NeedCopy-->
Step 6: Install NVIDIA GRID drivers
Enabling HDX™ 3D Pro requires you to install the NVIDIA GRID drivers on your hypervisor and on the VDA machines.
To install and configure the NVIDIA GRID Virtual GPU Manager (the host driver) on the specific hypervisors, see the following guides:
To install and configure the NVIDIA GRID guest VM drivers, perform the following general steps:
- Ensure that the guest VM is shut down.
- In the hypervisor control panel, allocate a GPU to the VM.
- Start the VM.
- Install the guest VM driver on the VM.
Step 7: Set up the runtime environment to complete the installation
After installing the Linux VDA package, configure the running environment by using the ctxinstall.sh script. You can run the script in interactive mode or silent mode.
Note:
Before setting up the runtime environment, ensure that the
en_US.UTF-8locale is installed in your OS. If the locale is not available in your OS, run thesudo locale-gen en_US.UTF-8command. For Debian, edit the/etc/locale.genfile by uncommenting the# en_US.UTF-8 UTF-8line and then run thesudo locale-gencommand.
Interactive mode:
There are two ways to use easy install in interactive mode:
- Run the
sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/sbin/ctxinstall.shcommand and type the relevant parameter at each prompt in the command line interface. - Run the
/opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/easyinstallcommand in the desktop environment of your VDA and then follow the instructions on the easy install GUI.
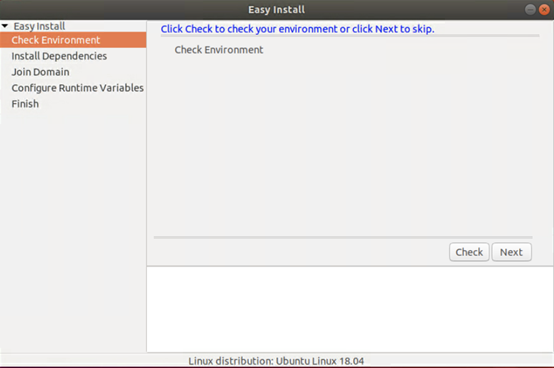
The easy install GUI guides you through the following operations:
- Check the system environment
- Install dependencies
- Join the VDA to a specified domain
- Configure the runtime environment
Silent mode:
To use easy install in silent mode, set the following environment variables before running ctxinstall.sh.
- CTX_EASYINSTALL_HOSTNAME=host-name – Denotes the host name of the Linux VDA server.
- CTX_EASYINSTALL_DNS=ip-address-of-dns – IP address of DNS.
- CTX_EASYINSTALL_NTPS=address-of-ntps – IP address or string name of the NTP server.
- CTX_EASYINSTALL_DOMAIN=domain-name – The NetBIOS name of the domain.
- CTX_EASYINSTALL_REALM=realm-name – The Kerberos realm name.
- CTX_EASYINSTALL_FQDN=ad-fqdn-name
- CTX_EASYINSTALL_ADINTEGRATIONWAY=winbind | sssd | centrify | pbis – Denotes the Active Directory integration method.
- CTX_EASYINSTALL_USERNAME=domain-user-name – Denotes the name of the domain user; used to join the domain.
- CTX_EASYINSTALL_PASSWORD=password – Specifies the password of the domain user; used to join the domain.
The ctxsetup.sh script uses the following variables:
- CTX_XDL_SUPPORT_DDC_AS_CNAME=Y | N – The Linux VDA supports specifying a Delivery Controller name using a DNS CNAME record.
- CTX_XDL_DDC_LIST=’list-ddc-fqdns’ – The Linux VDA requires a space-separated list of Delivery Controller Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDNs) to use for registering with a Delivery Controller. At least one FQDN or CNAME must be specified.
- CTX_XDL_VDA_PORT=port-number – The Linux VDA communicates with Delivery Controllers through a TCP/IP port.
- CTX_XDL_REGISTER_SERVICE=Y | N – The Linux Virtual Desktop services are started after machine startup.
- CTX_XDL_ADD_FIREWALL_RULES=Y | N – The Linux VDA services require incoming network connections to be allowed through the system firewall. You can open the required ports (by default ports 80 and 1494) automatically in the system firewall for the Linux Virtual Desktop.
- CTX_XDL_HDX_3D_PRO=Y | N – The Linux VDA supports HDX 3D Pro, a set of GPU acceleration technologies designed to optimize the virtualization of rich graphics applications. If HDX 3D Pro is selected, the VDA is configured for VDI desktops (single-session) mode - (that is, CTX_XDL_VDI_MODE=Y).
- CTX_XDL_VDI_MODE=Y | N – Whether to configure the machine as a dedicated desktop delivery model (VDI) or hosted shared desktop delivery model. For HDX 3D Pro environments, set the value to Y.
- CTX_XDL_SITE_NAME=dns-name – The Linux VDA discovers LDAP servers through DNS. To limit the DNS search results to a local Site, specify a DNS Site name. If unnecessary, set to <none>.
- CTX_XDL_LDAP_LIST=’list-ldap-servers’ – The Linux VDA queries DNS to discover LDAP servers. If DNS cannot provide LDAP service records, you can provide a space-separated list of LDAP FQDNs with LDAP ports. For example, ad1.mycompany.com:389 ad2.mycompany.com:3268 ad3.mycompany.com:3268. If you specify the LDAP port number as 389, the Linux VDA queries each LDAP server in the specified domain in polling mode. If there are x number of policies and y number of LDAP servers, the Linux VDA performs the total of X multiplied by Y queries. If the polling time exceeds the threshold, session logons might fail. To enable the faster LDAP queries, enable Global Catalog on a domain controller and specify the relevant LDAP port number as 3268. This variable is set to <none> by default.
- CTX_XDL_SEARCH_BASE=search-base-set – The Linux VDA queries LDAP through a search base set to the root of the Active Directory Domain (for example, DC=mycompany,DC=com). To improve search performance, you can specify a search base (for example, OU=VDI,DC=mycompany,DC=com). If unnecessary, set to <none>.
- CTX_XDL_FAS_LIST=’list-fas-servers’ – The Federated Authentication Service (FAS) servers are configured through AD Group Policy. The Linux VDA does not support AD Group Policy, but you can provide a semicolon-separated list of FAS servers instead. The sequence must be the same as configured in AD Group Policy. If any server address is removed, fill its blank with the <none> text string and do not modify the order of server addresses. To communicate with FAS servers properly, make sure you append a port number consistent with that specified on the FAS servers, for example, CTX_XDL_FAS_LIST=’fas_server_1_url:port_number; fas_server_2_url: port_number; fas_server_3_url: port_number’.
-
CTX_XDL_DOTNET_RUNTIME_PATH=path-to-install-dotnet-runtime – The path to install .NET Runtime 6.0 for supporting the new broker agent service (
ctxvda). The default path is /usr/bin. -
CTX_XDL_DESKTOP_ENVIRONMENT=gnome/gnome-classic/mate – Specifies the GNOME, GNOME Classic, or MATE desktop environment to use in sessions. If you leave the variable unspecified, the desktop currently installed on the VDA is used. However, if the currently installed desktop is MATE, you must set the variable value to mate.
You can also change the desktop environment for a target session user by completing the following steps:
- Create an
.xsessionor.Xclientsfile under the $HOME/<username> directory on the VDA. If you are using Amazon Linux 2, create an.Xclientsfile. If you are using other distributions, create an.xsessionfile. -
Edit the
.xsessionor.Xclientsfile to specify a desktop environment based on distributions.-
For MATE desktop
MSESSION="$(type -p mate-session)" if [ -n "$MSESSION" ]; then exec mate-session fi -
For GNOME Classic desktop
GSESSION="$(type -p gnome-session)" if [ -n "$GSESSION" ]; then export GNOME_SHELL_SESSION_MODE=classic exec gnome-session --session=gnome-classic fi -
For GNOME desktop
GSESSION="$(type -p gnome-session)" if [ -n "$GSESSION" ]; then exec gnome-session fi
-
- Share the 700 file permission with the target session user.
Starting with Version 2209, session users can customize their desktop environments.To enable this feature, you must install switchable desktop environments on the VDA in advance. For more information, see Custom desktop environments by session users.
- Create an
- CTX_XDL_START_SERVICE=Y | N – Whether or not the Linux VDA services are started when the configuration is complete.
- CTX_XDL_TELEMETRY_SOCKET_PORT – The socket port for listening for Citrix Scout. The default port is 7503.
- CTX_XDL_TELEMETRY_PORT – The port for communicating with Citrix Scout. The default port is 7502.
If any parameters are not set, the installation rolls back to interactive mode, with a prompt for user input. When all parameters are already set through the environment variables, the ctxinstall.sh script still prompts for user input for the path to install .NET Runtime 6.0.
In silent mode, you must run the following commands to set environment variables and then run the ctxinstall.sh script.
export CTX_EASYINSTALL_HOSTNAME=host-name
export CTX_EASYINSTALL_DNS=ip-address-of-dns
export CTX_EASYINSTALL_NTPS=address-of-ntps
export CTX_EASYINSTALL_DOMAIN=domain-name
export CTX_EASYINSTALL_REALM=realm-name
export CTX_EASYINSTALL_FQDN=ad-fqdn-name
export CTX_EASYINSTALL_ADINTEGRATIONWAY=winbind | sssd | centrify | pbis
export CTX_EASYINSTALL_USERNAME=domain-user-name
export CTX_EASYINSTALL_PASSWORD=password
export CTX_XDL_SUPPORT_DDC_AS_CNAME=Y | N
export CTX_XDL_DDC_LIST='list-ddc-fqdns'
export CTX_XDL_VDA_PORT=port-number
export CTX_XDL_REGISTER_SERVICE=Y | N
export CTX_XDL_ADD_FIREWALL_RULES=Y | N
export CTX_XDL_HDX_3D_PRO=Y | N
export CTX_XDL_VDI_MODE=Y | N
export CTX_XDL_SITE_NAME=dns-site-name | '<none>'
export CTX_XDL_LDAP_LIST='list-ldap-servers' | '<none>'
export CTX_XDL_SEARCH_BASE=search-base-set | '<none>'
export CTX_XDL_FAS_LIST='list-fas-servers' | '<none>'
export CTX_XDL_DOTNET_RUNTIME_PATH=path-to-install-dotnet-runtime
export CTX_XDL_DESKTOP_ENVIRONMENT= gnome | gnome-classic | mate | '<none>'
export CTX_XDL_TELEMETRY_SOCKET_PORT=port-number
export CTX_XDL_TELEMETRY_PORT=port-number
export CTX_XDL_START_SERVICE=Y | N
sudo -E /opt/Citrix/VDA/sbin/ctxinstall.sh
<!--NeedCopy-->
When running the sudo command, type the -E option to pass the existing environment variables to the new shell it creates. We recommend that you create a shell script file from the preceding commands with #!/bin/bash as the first line.
Alternatively, you can specify all parameters by using a single command:
sudo CTX_XDL_SUPPORT_DDC_AS_CNAME=Y|N \
CTX_XDL_DDC_LIST='list-ddc-fqdns' \
CTX_XDL_VDA_PORT=port-number \
CTX_XDL_REGISTER_SERVICE=Y|N \
CTX_XDL_ADD_FIREWALL_RULES=Y|N \
CTX_XDL_AD_INTEGRATION=1|2|3|4 \
CTX_XDL_HDX_3D_PRO=Y|N \
CTX_XDL_VDI_MODE=Y|N \
CTX_XDL_SITE_NAME=dns-name \
CTX_XDL_LDAP_LIST='list-ldap-servers' \
CTX_XDL_SEARCH_BASE=search-base-set \
CTX_XDL_FAS_LIST='list-fas-servers' \
CTX_XDL_DOTNET_RUNTIME_PATH=path-to-install-dotnet-runtime \
CTX_XDL_DESKTOP_ENVIRONMENT=gnome|gnome-classic|mate \
CTX_XDL_TELEMETRY_SOCKET_PORT=port-number \
CTX_XDL_TELEMETRY_PORT=port-number \
CTX_XDL_START_SERVICE=Y|N \
/opt/Citrix/VDA/sbin/ctxsetup.sh
<!--NeedCopy-->
Step 8: Run XDPing
Run sudo /opt/Citrix/VDA/bin/xdping to check for common configuration issues with a Linux VDA environment. For more information, see XDPing.
Step 9: Run the Linux VDA
Start the Linux VDA:
To start the Linux VDA services:
sudo /sbin/service ctxhdx start
sudo /sbin/service ctxvda start
<!--NeedCopy-->
Stop the Linux VDA:
To stop the Linux VDA services:
sudo /sbin/service ctxvda stop
sudo /sbin/service ctxhdx stop
<!--NeedCopy-->
Note:
Before you stop the
ctxvdaandctxhdxservices, run theservice ctxmonitorservice stopcommand to stop the monitor service daemon. Otherwise, the monitor service daemon restarts the services you stopped.
Restart the Linux VDA:
To restart the Linux VDA services:
sudo /sbin/service ctxvda stop
sudo /sbin/service ctxhdx restart
sudo /sbin/service ctxvda start
<!--NeedCopy-->
Check the status of the Linux VDA:
To check the running status of the Linux VDA services:
sudo /sbin/service ctxvda status
sudo /sbin/service ctxhdx status
<!--NeedCopy-->
Step 10: Create machine catalogs in Citrix Virtual Apps or Citrix Virtual Desktops™
The process for creating machine catalogs and adding Linux VDA machines is similar to the traditional Windows VDA approach. For a more detailed description of how to complete these tasks, see Create machine catalogs and Manage machine catalogs.
For creating machine catalogs that contain Linux VDA machines, there are a few restrictions that differentiate the process from creating machine catalogs for Windows VDA machines:
- For the operating system, select:
- The Multi-session OS option for a hosted shared desktops delivery model.
- The Single-session OS option for a VDI dedicated desktop delivery model.
- Do not mix Linux and Windows VDA machines in the same machine catalog.
Note:
Early versions of Citrix Studio did not support the notion of a “Linux OS.” However, selecting the Windows Server OS or Server OS option implies an equivalent hosted shared desktops delivery model. Selecting the Windows Desktop OS or Desktop OS option implies a single user per machine delivery model.
Tip:
If you remove and rejoin a machine to the Active Directory domain, you must remove and add the machine to the machine catalog again.
Step 11: Create delivery groups in Citrix Virtual Apps™ or Citrix Virtual Desktops
The process for creating a delivery group and adding machine catalogs containing Linux VDA machines is almost identical to Windows VDA machines. For a more detailed description of how to complete these tasks, see Create delivery groups.
For creating delivery groups that contain Linux VDA machine catalogs, the following restrictions apply:
- Ensure that the AD users and groups that you select have been properly configured to log on to the Linux VDA machines.
- Do not allow logon of unauthenticated (anonymous) users.
- Do not mix the delivery group with machine catalogs that contain Windows machines.
Important:
Publishing applications is supported with Linux VDA Version 1.4 and later. However, the Linux VDA does not support the delivery of desktops and apps to the same machine.
For information about how to create machine catalogs and delivery groups, see Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops 7 2206.
Troubleshooting
Use the information in this section to troubleshoot issues that can arise from using the easy install feature.
Joining a domain by using SSSD fails
An error might occur when you attempt to join a domain, with the output similar to the following (verify logs for screen printing):
Step 6: join Domain!Enter ctxadmin's password:Failed to join domain: failed to lookup DC info for domain 'CITRIXLAB.LOCAL' over rpc: The network name cannot be found
/var/log/xdl/vda.log:
2016-11-04 02:11:52.317 [INFO ] - The Citrix Desktop Service successfully obtained the following list of 1 delivery controller(s) with which to register: 'CTXDDC.citrixlab.local (10.158.139.214)'.
2016-11-04 02:11:52.362 [ERROR] - RegistrationManager.AttemptRegistrationWithSingleDdc: Failed to register with http://CTXDDC.citrixlab.local:80/Citrix/CdsController/IRegistrar. Error: General security error (An error occurred in trying to obtain a TGT: Client not found in Kerberos database (6))
2016-11-04 02:11:52.362 [ERROR] - The Citrix Desktop Service cannot connect to the delivery controller 'http://CTXDDC.citrixlab.local:80/Citrix/CdsController/IRegistrar' (IP Address '10.158.139.214')
Check the following:- The system clock is in sync between this machine and the delivery controller.
- The Active Directory provider (e.g. winbind daemon) service is running and correctly configured.
- Kerberos is correctly configured on this machine.
If the problem persists, please refer to Citrix Knowledge Base article CTX117248 for further information.
Error Details:
Exception 'General security error (An error occurred in trying to obtain a TGT: Client not found in Kerberos database (6))' of type 'class javax.xml.ws.soap.SOAPFaultException'.
2016-11-04 02:11:52.362 [INFO ] - RegistrationManager.AttemptRegistrationWithSingleDdc: The current time for this VDA is Fri Nov 04 02:11:52 EDT 2016.
Ensure that the system clock is in sync between this machine and the delivery controller.
Verify the NTP daemon is running on this machine and is correctly configured.
2016-11-04 02:11:52.364 [ERROR] - Could not register with any controllers. Waiting to try again in 120000 ms. Multi-forest - false
2016-11-04 02:11:52.365 [INFO ] - The Citrix Desktop Service failed to register with any controllers in the last 470 minutes.
<!--NeedCopy-->
/var/log/messages:
Nov 4 02:15:27 RH-WS-68 [sssd[ldap_child[14867]]]: Failed to initialize credentials using keytab [MEMORY:/etc/krb5.keytab]: Client 'RH-WS-68$@CITRIXLAB.LOCAL' not found in Kerberos database. Unable to create GSSAPI-encrypted LDAP connection.Nov 4 02:15:27 RH-WS-68 [sssd[ldap_child[14867]]]: Client 'RH-WS-68$@CITRIXLAB.LOCAL' not found in Kerberos database
To resolve this issue:
- Run the
rm -f /etc/krb5.keytabcommand. - Run the
net ads leave $REALM -U $domain-administratorcommand. - Remove the machine catalog and delivery group on the Delivery Controller.
- Run /opt/Citrix/VDA/sbin/ctxinstall.sh.
- Create the machine catalog and delivery group on the Delivery Controller.
Ubuntu desktop sessions show a gray screen
This issue occurs when you launch a session that is then blocked in a blank desktop. In addition, the console of the machine also shows a gray screen when you log on by using a local user account.
To resolve this issue:
- Run the
sudo apt-get updatecommand. - Run the
sudo apt-get install unity lightdmcommand. - Add the following line to
/etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf:
greeter-show-manual-login=true
Attempts to launch Ubuntu desktop sessions fail due to a missing home directory
/var/log/xdl/hdx.log:
2016-11-02 13:21:19.015 <P22492:S1> citrix-ctxlogin: StartUserSession: failed to change to directory(/home/CITRIXLAB/ctxadmin) errno(2)
2016-11-02 13:21:19.017 <P22227> citrix-ctxhdx: logSessionEvent: Session started for user ctxadmin.
2016-11-02 13:21:19.023 <P22492:S1> citrix-ctxlogin: ChildPipeCallback: Login Process died: normal.
2016-11-02 13:21:59.217 <P22449:S1> citrix-ctxgfx: main: Exiting normally.
<!--NeedCopy-->
Tip:
The root cause of this issue is that the home directory is not created for the domain administrator.
To resolve this issue:
-
From a command line, type pam-auth-update.
-
In the resulting dialog, verify that Create home directory login is selected.
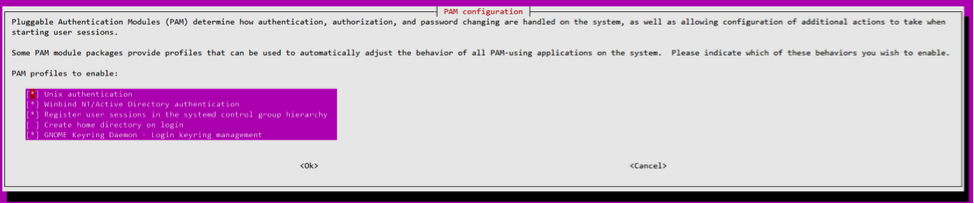
Session does not launch or ends quickly with dbus error
/var/log/messages (for RHEL or CentOS):
Oct 27 04:17:16 CentOS7 citrix-ctxhdx[8978]: Session started for user CITRIXLAB\ctxadmin.
Oct 27 04:17:18 CentOS7 kernel: traps: gnome-session[19146] trap int3 ip:7f89b3bde8d3 sp:7fff8c3409d0 error:0
Oct 27 04:17:18 CentOS7 gnome-session[19146]: ERROR: Failed to connect to system bus: Exhausted all available authentication mechanisms (tried: EXTERNAL, DBUS_COOKIE_SHA1, ANONYMOUS) (available: EXTERNAL, DBUS_COOKIE_SHA1, ANONYMOUS)#012aborting...
Oct 27 04:17:18 CentOS7 gnome-session: gnome-session[19146]: ERROR: Failed to connect to system bus: Exhausted all available authentication mechanisms (tried: EXTERNAL, DBUS_COOKIE_SHA1, ANONYMOUS) (available: EXTERNAL, DBUS_COOKIE_SHA1, ANONYMOUS)
Oct 27 04:17:18 CentOS7 gnome-session: aborting...
Oct 27 04:17:18 CentOS7 citrix-ctxgfx[18981]: Exiting normally.
Oct 27 04:17:18 CentOS7 citrix-ctxhdx[8978]: Session stopped for user CITRIXLAB\ctxadmin.
<!--NeedCopy-->
Or, alternately for Ubuntu distributions, use the log /var/log/syslog:
Nov 3 11:03:52 user01-HVM-domU pulseaudio[25326]: [pulseaudio] pid.c: Stale PID file, overwriting.
Nov 3 11:03:52 user01-HVM-domU pulseaudio[25326]: [pulseaudio] bluez5-util.c: Failed to get D-Bus connection: Did not receive a reply. Possible causes include: the remote application did not send a reply, the message bus security policy blocked the reply, the reply timeout expired, or the network connection was broken.
Nov 3 11:03:52 user01-HVM-domU pulseaudio[25326]: [pulseaudio] hashmap.c: Assertion 'h' failed at pulsecore/hashmap.c:116, function pa_hashmap_free(). Aborting.
Nov 3 11:03:52 user01-HVM-domU pulseaudio[25352]: [pulseaudio] core-util.c: Failed to connect to system bus: Did not receive a reply. Possible causes include: the remote application did not send a reply, the message bus security policy blocked the reply, the reply timeout expired, or the network connection was broken.
Nov 3 11:03:52 user01-HVM-domU pulseaudio[25352]: message repeated 10 times: [ [pulseaudio] core-util.c: Failed to connect to system bus: Did not receive a reply. Possible causes include: the remote application did not send a reply, the message bus security policy blocked the reply, the reply timeout expired, or the network connection was broken.]
Nov 3 11:03:52 user01-HVM-domU pulseaudio[25352]: [pulseaudio] pid.c: Daemon already running.Nov 3 11:03:58 user01-HVM-domU citrix-ctxgfx[24693]: Exiting normally
<!--NeedCopy-->
Some groups or modules do not take effect until a restart. If the dbus error messages appear in the log, we recommend that you restart the system and retry.
SELinux prevents SSHD from accessing the home directory
The user can launch a session but cannot log on.
/var/log/ctxinstall.log:
Jan 25 23:30:31 yz-rhel72-1 setroubleshoot[3945]: SELinux is preventing /usr/sbin/sshd from setattr access on the directory /root. For complete SELinux messages. run sealert -l 32f52c1f-8ff9-4566-a698-963a79f16b81
Jan 25 23:30:31 yz-rhel72-1 python[3945]: SELinux is preventing /usr/sbin/sshd from setattr access on the directory /root.
***** Plugin catchall_boolean (89.3 confidence) suggests ******************
If you want to allow polyinstantiation to enabled
Then you must tell SELinux about this by enabling the 'polyinstantiation_enabled' boolean.
You can read 'None' man page for more details.
Do
setsebool -P polyinstantiation_enabled 1
***** Plugin catchall (11.6 confidence) suggests **************************
If you believe that sshd should be allowed setattr access on the root directory by default.
Then you should report this as a bug.
You can generate a local policy module to allow this access.
Do
allow this access for now by executing:
# grep sshd /var/log/audit/audit.log | audit2allow -M mypol
# semodule -i mypol.pp
<!--NeedCopy-->
To resolve this issue:
-
Disable SELinux by making the following change to /etc/selinux/config.
SELINUX=disabled
-
Restart the VDA.
In this article
- Step 1: Prepare configuration information and the Linux machine
- Step 2: Prepare the hypervisor
- Step 3: Install .NET Runtime 6.0 as a prerequisite
- Step 4: Download the Linux VDA package
- Step 5: Install the Linux VDA package
- Step 6: Install NVIDIA GRID drivers
- Step 7: Set up the runtime environment to complete the installation
- Step 8: Run XDPing
- Step 9: Run the Linux VDA
- Step 10: Create machine catalogs in Citrix Virtual Apps or Citrix Virtual Desktops™
- Step 11: Create delivery groups in Citrix Virtual Apps™ or Citrix Virtual Desktops
- Troubleshooting