Browser content redirection
Browser content redirection prevents the rendering of webpages in the allow list on the VDA side. This feature uses Citrix Workspace™ app for Windows or Citrix Workspace app for Linux to instantiate a corresponding rendering engine on the client side, which fetches the HTTP and HTTPS content from the URL.
Note:
You can specify that webpages be redirected to the VDA side (and not redirected on the client side) by using a block list.
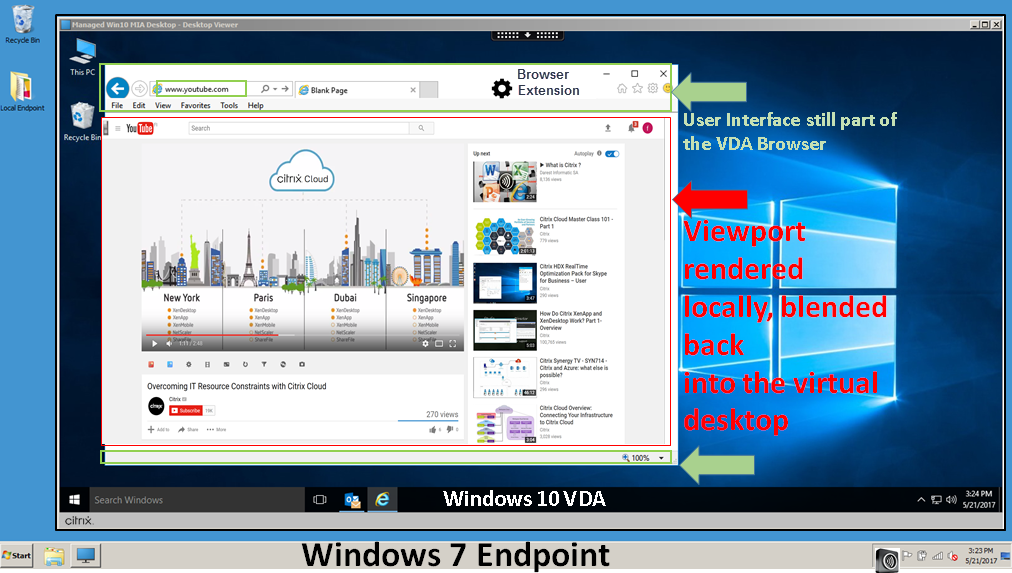
This overlay web layout engine runs on the endpoint device instead of on the VDA and uses the endpoint CPU, GPU, RAM, and Network.
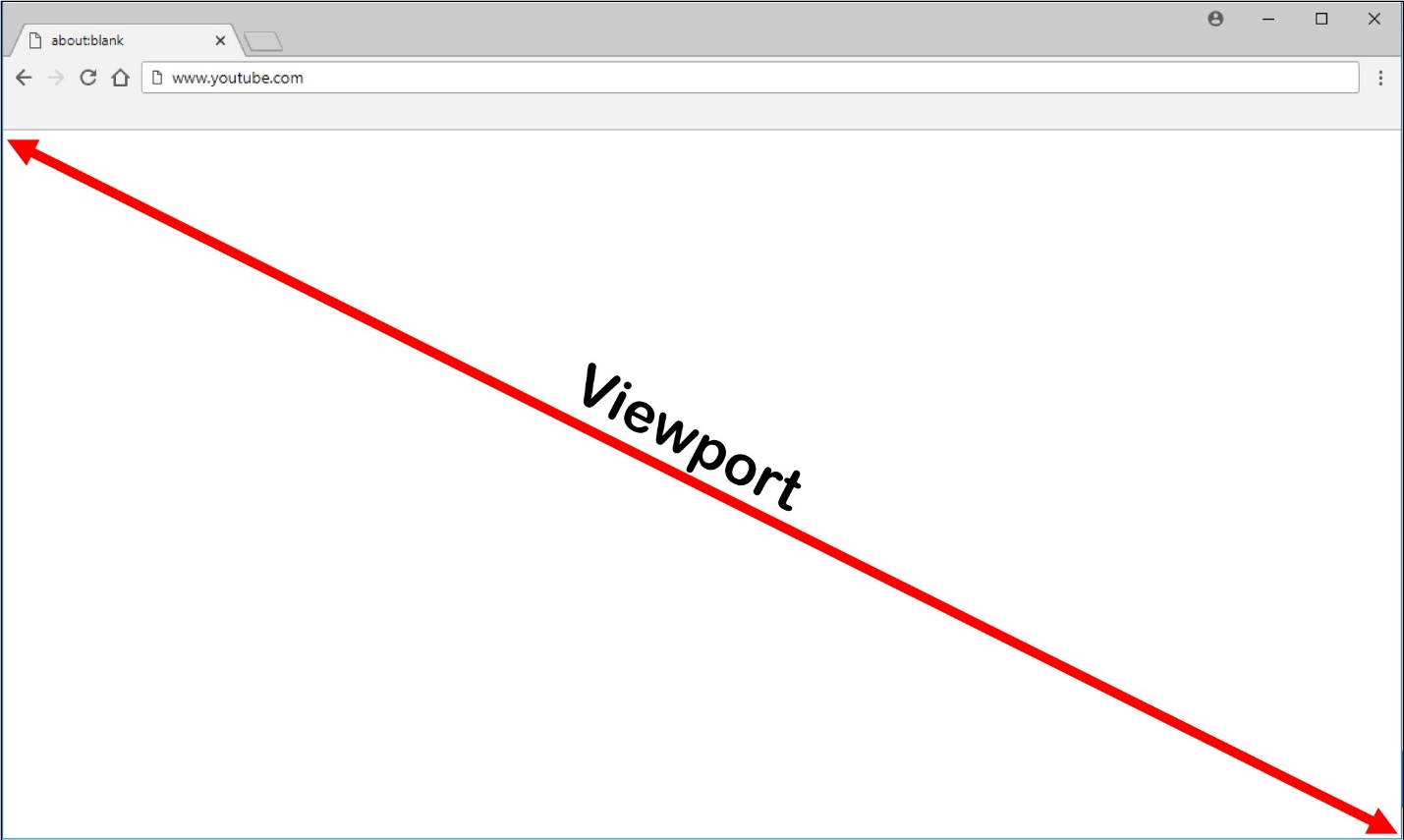
Only the browser viewport is redirected. The viewport is the rectangular area in your browser where content displays. The viewport doesn’t include things like the Address Bar, Favorites Toolbar, Status Bar. Those items are in the user interface, which are still running on the browser in the VDA.
- Configure a Studio policy that specifies an Access Control List containing the URLs in the allow list for redirection or the block list that disables redirection for specific URL paths. For the browser on the VDA to detect that the URL that the user is navigating to match the allow list or does not match a block list, a browser extension performs the comparison. The browser extension for Internet Explorer 11 is included in the installation media and is installed automatically. For Chrome, the browser extension is available in the Chrome Web Store, and you can deploy it using the Group Policies and ADMX files. Chrome extensions are installed on a per-user basis. Updating a golden image to add or remove an extension is not required.
- If a match is found in the allow list (for example
https://www.mycompany.com/), and there is no match to a URL in the block list (for examplehttps://www.mycompany.com/engineering), a virtual channel (CTXCSB) instructs the Citrix Workspace app that a redirection is required and relays the URL. Citrix Workspace app then instantiates a local rendering engine and displays the website. - Citrix Workspace app then blends back the website into the virtual desktop browser content area seamlessly.
Note:
For more information on what’s new and fixes for the browser content redirection extension, go to the Chrome Web Store and search “citrix® bcr” to find the extension.
The color of the logo specifies the status of the Chrome extension. It is one of these three colors:
- Green: Active and connected.
- Gray: Not active/idle on the current tab.
- Red: Broken/Not working.
You can debug logging by using Options in the extensions menu.
Here are scenarios of how the Citrix Workspace app fetches content:
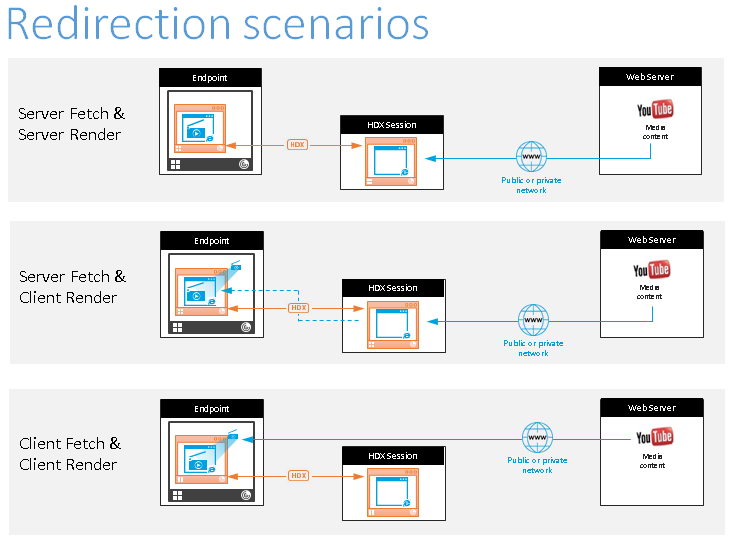
- Server fetch and server render: There is no redirection because you didn’t add the site to the allow list or the redirection failed. We fall back to rendering the webpage on the VDA and use Thinwire to remote the graphics. Use policies to control the fallback behavior. High CPU, RAM, and bandwidth consumption on the VDA.
-
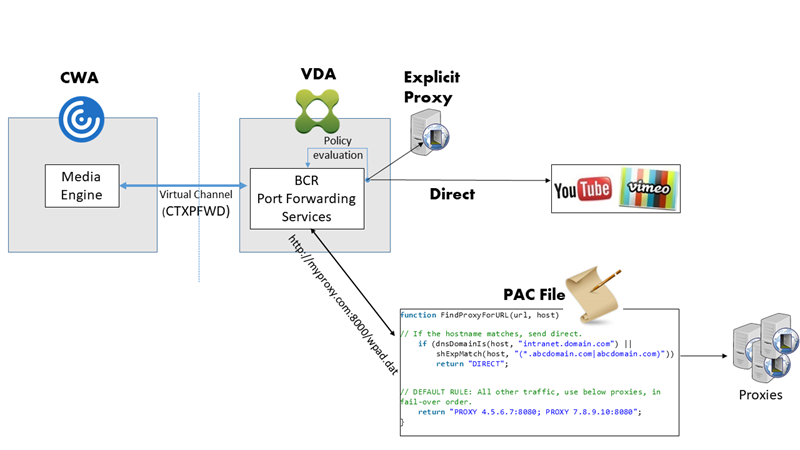
Server fetch and client render: Citrix Workspace app contacts and fetches content from the web server through the VDA using a virtual channel (CTXPFWD). This option is useful when the client doesn’t have internet access (for example, thin clients). Low CPU and RAM consumption on the VDA, but bandwidth is consumed on the ICA® virtual channel.
There are three modes of operation for this scenario. The term proxy refers to a proxy device that the VDA accesses to gain Internet access.
Which policy option to choose:
- Explicit Proxy - If you have a single explicit proxy in your data center.
- Direct or Transparent - If you do not have proxies, or if you use transparent proxies.
- PAC files - If you rely on PAC files so browsers in the VDA can automatically choose the appropriate proxy server for fetching a specified URL.
-
Client fetch and client render: Because the Citrix Workspace app contacts the web server directly, it requires internet access. This scenario offloads all the network, CPU, and RAM usage from your XenApp and XenDesktop® Site.
Benefits:
- Better end user experience (Adaptive Bit Rate (ABR))
- Reduced VDA resource usage (CPU/RAM/IO)
- Reduced bandwidth consumption
Fallback mechanism:
There might be times when client redirection fails. For example, if the client machine does not have direct internet access, an error response might go back to the VDA. In such cases, the browser on the VDA can then reload and render the page on the server.
You can suppress server rendering of video elements by using the existing Windows Media fallback prevention policy. Set this policy to Play all content only on client or Play only client-accessible content on client. These settings block video elements from playing on the server if there are failures in client redirection. This policy takes effect only when you enable browser content redirection and the Access Control List policy contains the URL that falls back. The URL can’t be in the block list policy.
System requirements:
Windows endpoints:
- Windows 10
- Citrix Workspace app 1809 for Windows or later
Note:
Browser content redirection is supported only on the Current Release of Citrix Workspace app for Windows, but not on the Citrix Workspace app LTSR releases, 1912 and 2203.1.
Linux endpoints:
- Citrix Workspace app 1808 for Linux or later
- Thin client terminals must include WebKitGTK+
Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops 7 1808 or later and XenApp and XenDesktop 7.15 CU5 or later:
-
VDA operating system: Windows 10 (minimum version 1607), Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019
-
Browser on the VDA:
-
Google Chrome v66 or later (Chrome requires Citrix Workspace app 1809 for Windows or later on the user endpoint, Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops™ 7 1808 VDA or later, and the browser content redirection extension)
-
Internet Explorer 11 and configure these options:
- Clear Enhanced Protected Mode under: Internet Options > Advanced > Security
- Check Enable third-party browser extensions under: Internet Options > Advanced > Browsing
-
Troubleshooting
For troubleshooting information, see the Knowledge Center article https://support.citrix.com/article/CTX230052
Browser content redirection Chrome extension
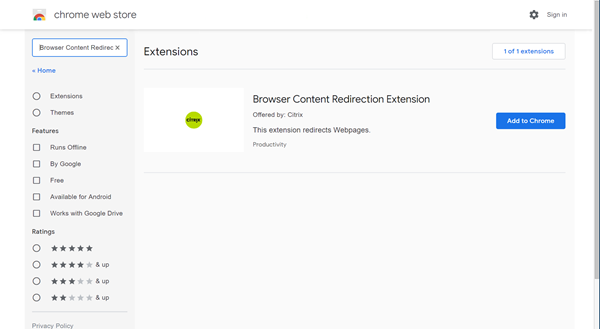
To use browser content redirection with Chrome, add the browser content redirection extension from the Chrome Web Store. Click Add to Chrome in the Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops environment.
The extension is not required on the user’s client machine – only in the VDA.
System requirements
- Chrome v66 or higher
- Browser content redirection extension
- Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops 7 1808 or higher
- Citrix Workspace app 1809 for Windows or higher
Note:
Browser content redirection is supported only on the Current Release of Citrix Workspace app for Windows, but not on the Citrix Workspace app LTSR releases, 1912 and 2203.1.
This method works for individual users. To deploy the extension to a large group of users in your organization, deploy the extension using Group Policy.
Deploy the extension using Group Policy
- Import the Google Chrome ADMX files into your environment. For information about downloading policy templates and installing and configuring the templates into your Group Policy Editor, see Set Chrome Browser policies on managed PCs.
-
Open your Group Policy Management console and go to User Configuration \ Administrative Templates\Classic Administrative Templates (ADM) \ Google\ Google Chrome \ Extensions. Enable the Configure the list of force-installed apps and extensions setting.
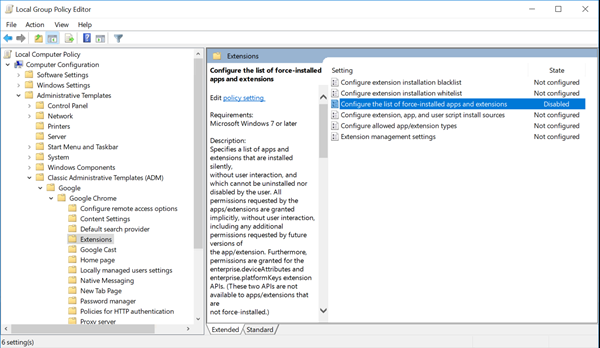
-
Click Show and type the following string, which corresponds to the extension ID. Update the URL for the browser content redirection extension.
hdppkjifljbdpckfajcmlblbchhledln; https://clients2.google.com/service/update2/crx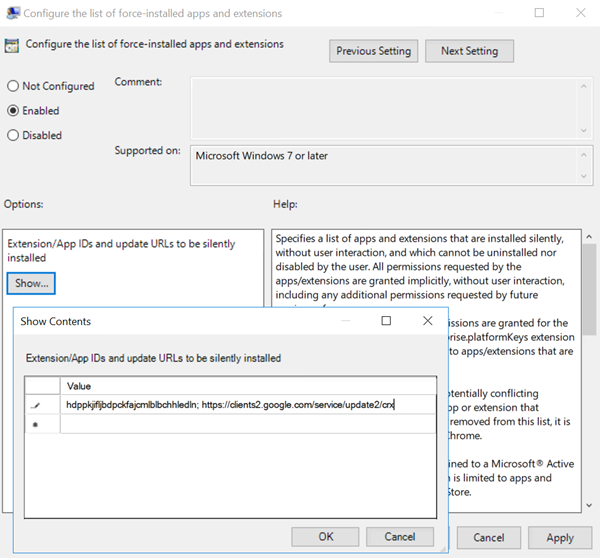
-
Apply the setting and after a gpupdate refresh, the user automatically receives the extension. If you launch the Chrome browser in the user’s session, the extension is already applied and they cannot remove it.
Any updates to the extension are automatically installed on the users’ machines through the update URL that you specified in the setting.
If the Configure the list of force-installed apps and extensions setting is set to Disabled, the extension is automatically removed from Chrome for all users.
Browser content redirection Edge Chromium extension
To install the browser content redirection extension in Edge, make sure you have version 83.0.478.37 or higher of the Edge browser installed.
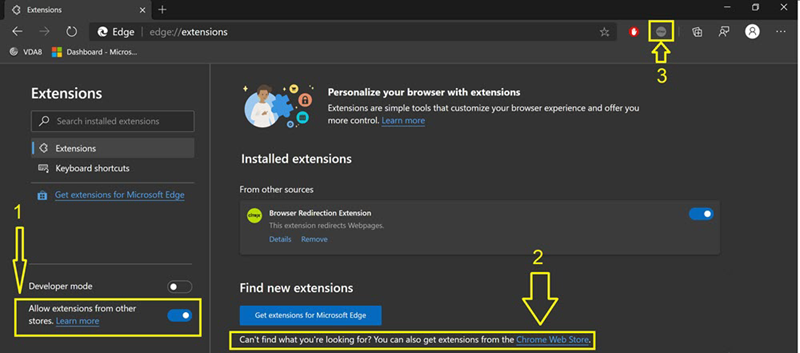
- Click the Extensions option. Choose Manage extension. Turn on Allow extensions from other stores.
- Click the Chrome Web Store link and the extension appears at the bar on the top right. For more info on Microsoft Edge extensions, see Extensions.
Browser content redirection and DPI
When using browser content redirection with the DPI (scaling) set to anything over 100% on the user’s machine, the redirected browser content screen displays incorrectly. To avoid this issue, do not set the DPI when using browser content redirection. Another way to avoid the issue is by disabling browser content redirection GPU acceleration for Chrome by creating the registry key on the user’s machine. For information, see Browser content redirection and DPI in the list of features managed through the registry.
Single sign-on with Integrated Windows Authentication
Browser content redirection enhances the overlay to use the Negotiate scheme for authentication to web servers configured with Integrated Windows Authentication (IWA) within the same domain as the VDA.
By default, browser content redirection uses a basic authentication scheme that requires users to authenticate with their VDA credentials each time they access the web server. For single sign-on, you can either enable the Browser content redirection Integrated Windows Authentication support policy setting or create a registry key on the VDA.
Before enabling single sign-on, complete the following:
- Configure the Kerberos infrastructure to issue tickets for service principal names (SPNs) constructed from the host name. For example,
HTTP/serverhostname.com. - For server fetch: When you use browser content redirection in server fetch mode, ensure that DNS is configured properly on the VDA.
- For client fetch: When you use browser content redirection in client fetch mode, ensure that DNS is configured properly on the client device and that you allow TCP connections from the overlay to the web server’s IP address.
To configure single sign-on using the Browser content redirection policy, see the Browser content redirection Integrated Windows Authentication support setting.
Alternatively, you can enable single sign-on to a web server by adding a registry key on the VDA. For information, see Single sign-on with Integrated Windows Authentication for browser content redirection in the list of features managed through the registry.
User-agent request header
The user-agent header helps identify HTTP requests sent from browser content redirection. This setting can be useful when you configure proxy and firewall rules. For example, if the server blocks the requests sent from browser content redirection, you can create a rule that contains the user-agent header to bypass certain requirements.
Only Windows devices support the user-agent request header.
By default, the user-agent request header string is disabled. To enable the user-agent header for client-rendered content, use the Registry editor. For information, see User-agent request header in the list of features managed through the registry.
Browser content redirection client compatibility
You can use WMI to check if your client is compatible with browser content redirection. Use any method for accessing WMI works. The following is an example using PowerShell.
- Open PowerShell.
- Run
Get-WmiObject -Class CTXBCRStatus. - Check the
BCR_Capableparameter.- If
True, the client is compatible with browser content redirection. - If
False, the client is not compatible with browser content redirection.
- If
Additional information
- If
CtxBrowserSvcis not available, no results are displayed when running the command. - If
CtxBrowserSvchas never been run, the results return an invalid class error.