Geo-location Routing
Geo-location routing allows administrators to direct user traffic to a specific region (PoPs) regardless of the user’s location. Geo-location routing can be used in the following scenarios:
-
Data residency requirements: Many countries have regulations requiring data to be stored and processed within their borders. For example, geo-location routing can be configured to ensure that all data from European Union (EU) users is routed to PoPs within the EU, complying with General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) data residency requirements.
-
Data sovereignty: Data is governed by the laws and regulations of the country or region where it is collected and processed. For instance, a multinational corporation can leverage geo-location routing to ensure that data from DaaS control regions like the United States, European Union, and Asia Pacific South is processed in the corresponding regional PoPs, complying with data sovereignty laws.
-
Industry-specific regulations: Certain industry-specific regulations require data to be stored and processed in specific ways. For example, a healthcare provider can use geo-location routing to ensure that patient data is routed to Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) compliant commercial region PoPs within the United States.
-
Financial services: Financial institutions are often subject to regulations that require financial data to be processed within specific jurisdictions. For example, a bank can use geo-location routing to ensure that transactions from Asia Pacific South customers are processed in commercial region PoPs within the Asia Pacific South, complying with local financial regulations.
-
Traffic optimization: Geo-location routing ensures that user traffic is directed to specific region PoPs, optimizing performance by reducing latency and improving user experience.
-
Load balancing: By directing traffic to specific region PoPs, administrators can distribute the load across multiple PoPs, preventing overloading of any single region.
Note:
Geo-location routing is available only for Citrix Cloud customers in commercial regions. It is not available for Google Cloud Platform, Japan, and US Government regions.
How to configure geo-location routing in Citrix Workspace
You can configure a specific region for the user traffic from the Resource locations or Workspace Configuration page on Citrix Cloud.
-
Sign in to Citrix Cloud.
-
Click the hamburger menu and select Resource Locations or Workspace Configuration.
-
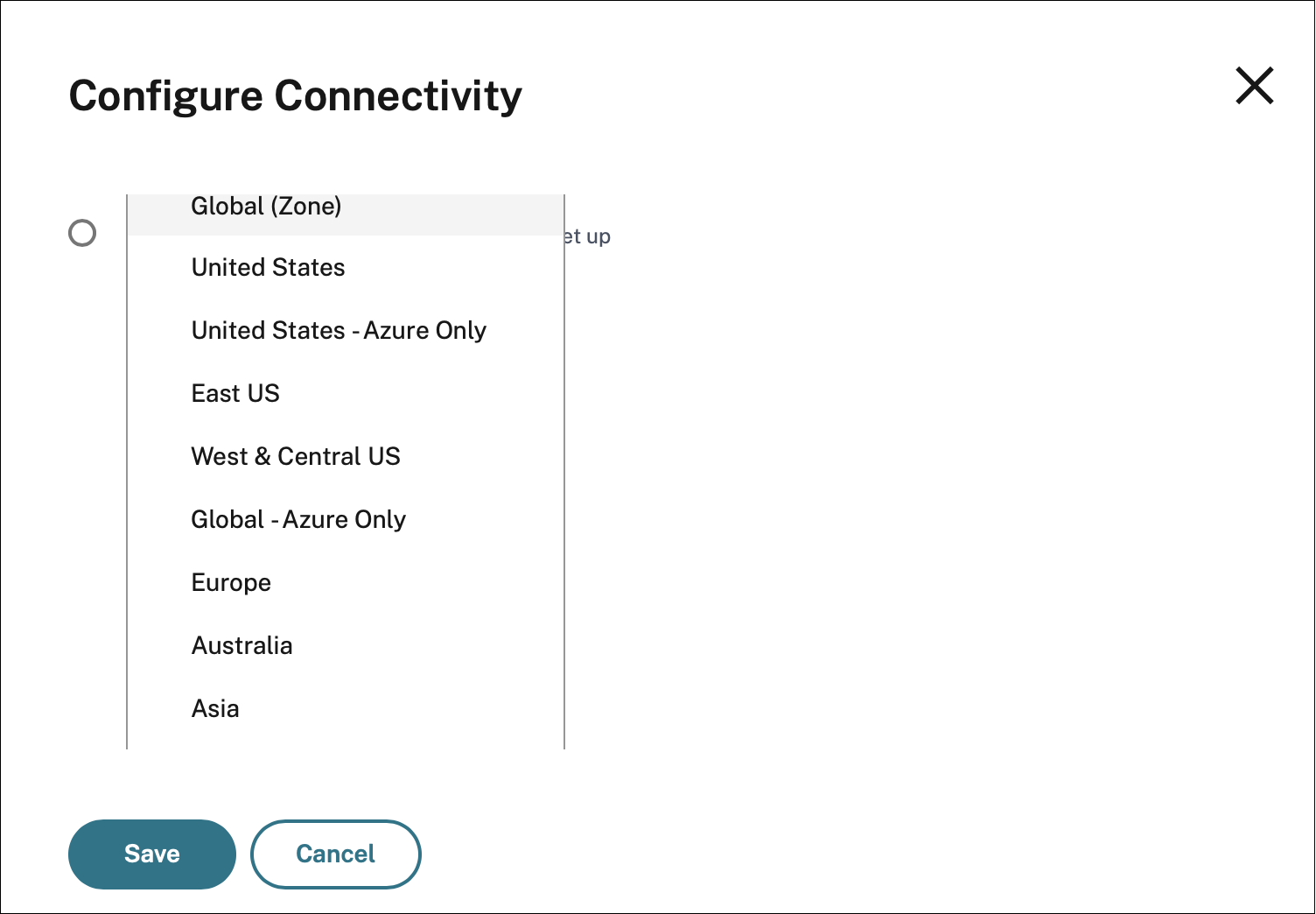
On the Resource Locations page, select a location and click Gateway. The Configure Connectivity screen appears.
-
In the Workspace Configuration page, in External Connectivity, select a location and click the ellipsis. The Configure Connectivity screen appears.
For the list of FQDNs associated with the PoPs that support geo-location based traffic routing, see Regional FQDNs for geo-location routing.
-
-
In Gateway Service Region (Optional), select the region to which you want to route your customer traffic.
Notes:
If you do not select any region, then Global is selected by default. When the region is Global, the traffic is diverted to the PoP that is in the closest proximity to the customer. For more information, see Optimal Gateway Routing.
In rare scenarios, if there is an outage, and all the PoPs of a specific region are not available, then the configuration falls back to Global instead of blocking the traffic.
-
Click Save.
How to configure geo-location routing in StoreFront™
Important:
Geo-location routing can be configured in StoreFront only when you enable Citrix Gateway service for StoreFront. For more information, see Citrix Gateway service for StoreFront.
StoreFront version 2503 and later supports geo-location routing.
You can manually specify the PoP FQDN for the region you want to use. For more information on how to configure geo-location routing in StoreFront, see Add Citrix Gateway Service.