Get started with Session Recording
After you perform the following steps, you can begin recording and reviewing XenApp and XenDesktop® sessions.
- Become familiar with the Session Recording components.
- Select the deployment scenario for your environment.
- Verify the installation requirements.
- Install the Windows roles and features prerequisites.
- Install Session Recording.
- Configure the Session Recording components to permit recording and viewing of sessions.
Session Recording consists of five components:
- Session Recording Agent. A component installed on each VDA for Server OS or Desktop OS to enable recording. It is responsible for recording session data.
-
Session Recording Server. A server that hosts:
- The Broker. An IIS 6.0+ hosted Web application that handles the search queries and file download requests from the Session Recording Player, handles policy administration requests from the Session Recording Policy Console, and evaluates recording policies for each XenApp and XenDesktop session.
- The Storage Manager. A Windows service that manages the recorded session files received from each Session Recording-enabled computer running XenApp® and XenDesktop.
- Administrator Logging. An optional subcomponent installed with the Session Recording Server to log the administration activities. All the logging data is stored in a separate SQL Server database named CitrixSessionRecordingLogging by default. You can customize the database name.
- Session Recording Player. A user interface that users access from a workstation to play recorded XenApp and XenDesktop session files.
- Session Recording Database. A component that manages the SQL Server database for storing recorded session data. When this component is installed, it creates a database named CitrixSessionRecording by default. You can customize the database name.
- Session Recording Policy Console. A console used to create policies to specify which sessions are recorded.
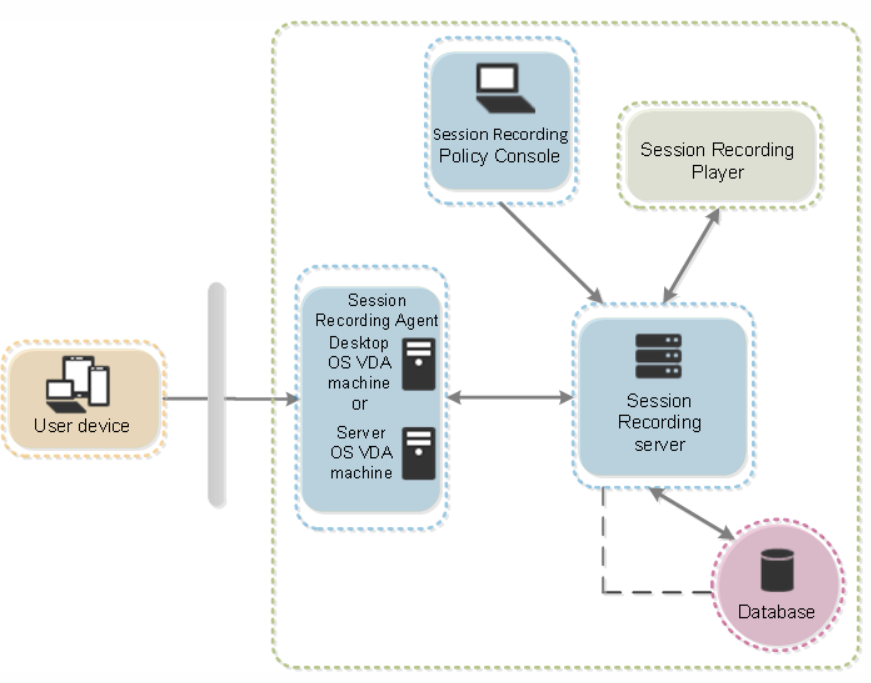
This illustration shows the Session Recording components and their relationship with each other:
In the deployment example illustrated here, the Session Recording Agent, Session Recording Server, Session Recording Database, Session Recording Policy Console, and Session Recording Player all reside behind a security firewall. The Session Recording Agent is installed on a VDA for Server OS or Desktop OS. A second server hosts the Session Recording Policy Console, a third server acts as the Session Recording Server, and a fourth server hosts the Session Recording Database. The Session Recording Player is installed on a workstation. A client device outside the firewall communicates with the VDA for Server OS on which the Session Recording Agent is installed. Inside the firewall, the Session Recording Agent, Session Recording Policy Console, Session Recording Player, and Session Recording Database all communicate with the Session Recording Server.