Administrative roles
The administrative role assigned to a group of users controls viewing and managing objects within a Citrix Provisioning™ server implementation. Citrix Provisioning uses groups that exist within the network, Windows, or Active Directory Groups. All members within a group have the same administrative privileges within a farm. An administrator has multiple roles if they belong to more than one group.
The following administrative roles can be assigned to a group:
- Farm administrator
- Farm read-only administrator
- Site administrator
- Device administrator
- Device operator
After a group is assigned an administrative role using the Citrix Provisioning console, certain requirements are required. If a member of that group attempts to connect to a different farm, a dialog displays requesting that you identify a provisioning server within that farm. Use either the Windows credentials you are currently logged in with, the default setting, or enter your Active Directory credentials. Citrix Provisioning does not support using both domain and workgroups simultaneously.
The role associated with the group determines your administrative privileges within this farm. Group role assignments can vary from farm to farm.
Managing farm administrators
Farm administrators view and manage all objects within a farm, and also create sites and manage role memberships throughout the entire farm. In the Citrix Provisioning console, administrators perform farm-level tasks.
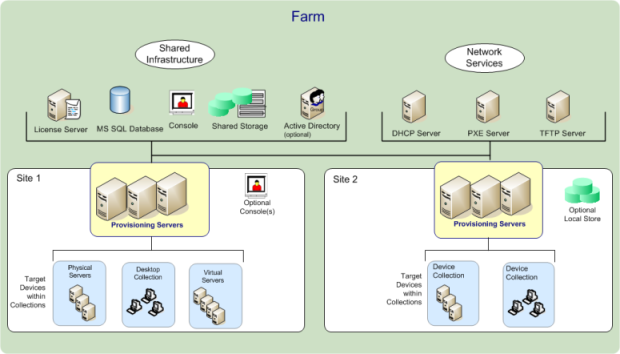
When the farm is first configured using the Configuration Wizard, the administrator that creates the farm is automatically assigned the Farm Administrator role. While configuring the farm, that administrator selects the option to use either Windows or Active Directory credentials for user authorization within the farm. After an administrator runs the Configuration Wizard, more groups can be assigned the farm administrator role in the console.
To assign more farm administrators
- In the console, right-click on the farm to which the administrator role is assigned, then select Properties. The Farm Properties dialog appears.
- On the Groups tab, highlight all the groups assigned administrative roles in this farm, then click Add. In the Add Systems Group dialog, add groups to give access rights. Click OK.
- On the Security tab, select the groups to which you want to provide read-only access. The groups that are not selected will have read-write access. Click Add if you want to add groups to the list.
- Click OK to close the dialog box.
Note:
The authorization method displays to indicate if Windows or Active Directory credentials are used for user authorization in this farm. The groups for administrative roles are limited to groups in the native domain and domains with a two-way trust to the native domain.
Managing site administrators
Site administrators have full management access to all the objects within a site. For example, the site administrator manages provisioning servers, site properties, target devices, device collections, virtual disk assignments pools.
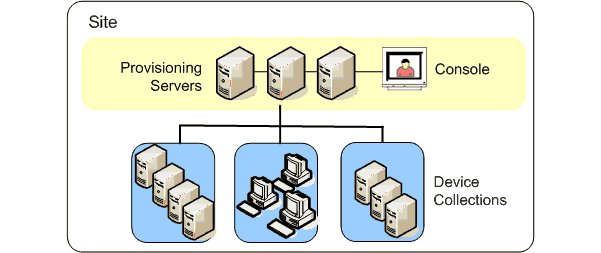
If a farm administrator assigns a site as the owner of a particular store, the site administrator can also manage that store. Managing a store includes adding and removing virtual disks from shared storage or assigning provisioning servers to the store. The site administrator can also manage device administrator and device operator memberships.
To assign the site administrator role to one or more groups and its members
- In the console, right-click on the site for which the administrator role is assigned, then select Properties. The Site Properties dialog appears.
- Click the Security tab, then click the Add button. The Add Security Group dialog appears.
- From the menu, select the groups to which you want to provide access.
- Optionally, repeat steps 2 and 3 to continue assigning more site administrators.
- Click OK to close the dialog.
Managing device administrators
Device administrators manage device collections to which they have privileges. Management tasks include assigning and removing a virtual disk from a device, editing device properties and viewing read-only virtual disk properties. Device collections consist of a logical grouping of devices. For example, a device collection might represent a physical location, a subnet range, or a logical grouping of target devices. A target device can only be a member of one device collection.
To assign the device administrator role to one or more groups and its members
- In the console, expand the site where the device collection exists, then expand the Device Collections folder.
- Right-click on the device collection that you want to add device administrators to, then select Properties. The Device Collection Properties dialog appears.
- On the Security tab, under the Groups with Device Administrator access list, click Add. The Add Security Group dialog appears.
- From the menu, select the groups to which you want to provide access.
- Click OK to close the dialog box.
Managing device operators
A device operator has administrator privileges to perform the following tasks within a device collection for which they have privileges:
- Boot and reboot a target device
- Shut down a target device
To assign the device operator role to one or more groups
- In the console, expand the site where the device collection exists, then expand the Device Collections folder.
- Right-click on the device collection that you want to add device operators to, then select Properties. The Device Collection Properties dialog appears.
- On the Security tab, under the Groups with Device Operator access list, click Add. The Add Security Group dialog appears.
- To assign a group the Device Operator role, select each system group that requires device operator privileges, then click OK.
- Click OK to close the dialog box.
Modifying the search approach for AD environments
For some AD environments containing configurations with complex nested groups and domains with many trust associations, the default method might be unable to find the user’s expected administrative memberships. To resolve such scenarios, use a registry setting to change the search approach:
- In the registry setting, locate
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Citrix\ProvisioningServices. - Create a DWORD named “DomainSelectOption”.
- In the
DomainSelectOption DWORD, set one of the following values (in decimal format) for the desired search approach:
- 0 – The default search. This method searches the user’s domain followed by administrative group domains.
- 1 – Search in the user’s domain and in the administrative group domain, followed by other trusted domains within a user’s domain.
- 2 – Obsolete.
- 3 – Search in the user’s domain followed by administrative group domains. The groups that are discovered are further enumerated over the parent’s domain.
- 4 – Search the user’s domain and in the administrative group domain, followed by other trusted domains within a user’s domain. The groups that are discovered are further enumerated over the parent’s domain.
- 5 - Search the user’s group membership from token groups in the user’s domain and in the administrative group domain.
- 6 - Search the user’s group membership from token groups in the user’s domain and in the administrative group domain, followed by other trusted domains within a user’s domain.
- 7 - Search the user’s group membership directly from authorization groups.
- 8 - Search the user’s group membership directly as “Member Of” groups.
About whitelist methods
Use the information in this section for diagnostic purposes only. Sometimes, it may helpful to specify a specific domain for a user group to search against. To perform this task, update the registry and provide a JSON file for the white list domain. Use only the default search option. If you are providing a black list domain, it is excluded from the white list domains. No search occurs when the end list is empty.
In the registry:
- Locate
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Citrix\ProvisioningServices. - Create a DWORD entry WhitelistOnly. Set the value to 1 to enable white list search.