Configure centralized site management using PowerShell scripts
To set up centralized site management using PowerShell scrips, follow these steps:
-
Decide which site will serve as the primary site. That decision can be affected by various reasons, such as geography (region) and network resources.
-
Verify current aggregation: Run the
Getscript to determine which sites (if any) are currently aggregated to a primary site. -
To enable and configure a site aggregation for centralized site management in both the Full Configuration and the Monitor UIs, customize and run the
Post to servicescript for each primiary-and-secondary-site pair. -
To enable and configure a site aggregation for centralized site management through a unified Citrix Workspace URL, customize and run the
Post to Citrix Cloudscript for each primiary-and-secondary-site pair. -
Run the Get script again to verify the setup of the intended aggregation.
To remove an aggregation, perform the following steps as needed:
-
Remove an aggregation from Citrix DaaS: Customize and run the
Delete from servicescript to remove an aggregation in the Citrix DaaS. -
Remove an aggregation from Citrix Cloud: Customize and run a
Delete from Citrix Cloudscript to remove an aggregation from Citrix Cloud.
Preparation
Before you begin, you need to have:
- Full administrator access to the primary and secondary sites (the instances of the Citrix DaaS).
- Familiarity with Citrix Cloud and basic PowerShell principles.
- Windows PowerShell Integrated Scripting Environment (ISE).
- Items used by Citrix Cloud Services APIs. For guidance, see the API documentation overview. To customize the scripts, you need:
- Customer IDs of your Citrix DaaS instances.
- Bearer token value (
CWSAuth) used for authentication and authorization when calling APIs. To learn how to retrieve your CitrixCWSAuthvalue, see CTX330675.
Configuration example
An administrator wants to aggregate five instances of the Citrix DaaS. Each instance is considered a customer.
- This example refers to the customers as A, B, C, D, and E.
- The administrator decides that customer C will be the hub. A, B, D, and E will be the spoke sites.
- This is the first time that instances are being aggregated.
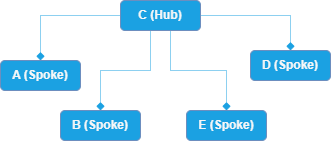
- Because this is the first time the service instances are being aggregated, the administrator knows that there are no existing enumerations (links from spokes to the hub). Otherwise, the administrator would customize and run the Get script to ensure that there are no enumerations.
-
The administrator customizes and runs the Post to Citrix Cloud script, once for each spoke customer, to set up the aggregation in Citrix Cloud. Each time, the script indicates the bearer token, the customer ID of the hub (customer C), and the customer ID of a non-hub customer (customer A, B, D, or E).
- Post to Citrix Cloud script #1: Specifies the bearer token, the customer ID of the customer A (spoke), and the customer ID of customer C (hub).
- Post to Citrix Cloud script #2: Specifies the bearer token, the customer ID of the customer B (spoke), and the customer ID of customer C (hub).
- Post to Citrix Cloud script #3: Specifies the bearer token, the customer ID of the customer D (spoke), and the customer ID of customer C (hub).
- Post to Citrix Cloud script #4: Specifies the bearer token, the customer ID of the customer E (spoke), and the customer ID of customer C (hub).
-
The administrator customizes and runs the Post to service script, once for each spoke customer, to set up the aggregation in the Citrix DaaS. Each time, the script indicates the bearer token, the customer ID of the hub (customer C), and the customer ID of a non-hub customer (customer A, B, D, or E).
- Post to service script #1: Specifies the bearer token, the customer ID of customer A (spoke), and the customer ID of customer C (hub).
- Post to service script #2: Specifies the bearer token, the customer ID of customer B (spoke), and the customer ID of customer C (hub).
- Post to service script #3: Specifies the bearer token, the customer ID of customer D (spoke), and the customer ID of customer C (hub).
- Post to service script #4: Specifies the bearer token, the customer ID of customer E (spoke), and the customer ID of customer C (hub).
-
After running the four Post to Citrix Cloud and four Post to service scripts, the administrator runs the Get script with the bearer token and the customer ID of the hub (customer C).
The script output lists the four spoke customers (A, B, D, and E).
-
Later, the administrator decides to remove a spoke (customer E) from the aggregation. (As a precaution, the administrator might run the Get script first, to verify that customer E is still being aggregated.)
-
The administrator customizes the Delete from service script to specify the bearer token, the customer ID of customer E (spoke to be removed), and the customer ID of customer C (hub). That script removes the enumeration of customer E from the service.
-
After successfully running the Delete from service script, the administrator customizes and runs the Delete from Citrix Cloud script to remove the enumeration of customer E from Citrix Cloud.
After running the Delete scripts, the administrator runs the Get script to ensure that customer A, B, and D remain as a spoke to hub C.
-
Verify current aggregation
The Get script displays current aggregation information, if any.
Get script
$headers = @{}
$headers.Add("Accept","application/json")
$headers.Add("Content-Type","application/json")
$headers.Add("Authorization","CWSAuth bearer=XXXXXXX")
$uri = "https://trust.citrixworkspacesapi.net/CustomerID/links"
$resp = Invoke-WebRequest -Method Get -Uri $uri -Headers $headers
Write-Host "Citrix Cloud Status Code: $($resp.RawContent)"
$uri = "https://resourceprovider.apps.cloud.com/CustomerID/aggregation"
$resp = Invoke-WebRequest -Method Get -Uri $uri -Headers $headers
Write-Host "CVAD Status Code: $($resp.RawContent)"
<!--NeedCopy-->
Prepare and run the Get script
- Open the PowerShell ISE and paste the Get script into the working pane.
- On line 4, replace
CWSAuth bearer=XXXXXXXwith yourCWSAuthvalue (for example,CWSAuth bearer=AbCdef123Ghik…). This value is a long hash that resembles a certificate key. - On lines 6 and 10, replace
CustomerIDwith the customer ID of the primary site. - Run the script.
Expected output:
- If the site does not have an enumeration,
linkedCustomerandSPOKE-CUSTOMER IDare empty. - If the site has an enumeration, the customer ID of the secondary site is shown.
Set up an aggregation in Citrix Cloud
To set up a site aggregation in Citrix Cloud, run the Post to Citrix Cloud script. This script links a primary site with a secondary site in Citrix Cloud. As a result, end users can view and access their apps and desktops from both the primary and the secondary sites through the Citrix Workspace URL for the primary site.
Post to Citrix Cloud script
$headers = @{}
$headers.Add("Accept","application/json")
$headers.Add("Content-Type","application/json")
$headers.Add("Authorization","CWSAuth bearer=XXXXXXX")
$uri = "https://trust.citrixworkspacesapi.net/HubCustomerID/links"
$resp = Invoke-RestMethod -Method Get -Uri $uri -Headers $headers
$allLinks = $resp.linkedCustomers + @("SpokeCustomerID")
$body = @{"customers"=$allLinks}
$bodyjson = $body | ConvertTo-Json
$resp = Invoke-WebRequest -Method Post -Uri $uri -Headers $headers -Body $bodyjson -ContentType 'application/json'
Write-Host "Citrix Cloud Status Code: $($resp.RawContent)"
<!--NeedCopy-->
Prepare and run the Post to Citrix Cloud script
- Open the PowerShell ISE and paste the Post to Citrix Cloud script into the working pane.
- On line 4, replace
CWSAuth bearer=xxxxxxx1with yourCWSAuthvalue (for example,CWSAuth bearer=AbCdef123Ghik…). This value is a long hash that resembles a certificate key. - On line 6, replace
HubCustomerIDwith the customer ID of the primary site. - On line 9, replace
SpokeCustomerIDwith the customer ID of the secondary site. - Run the script.
Set up an aggregation in the Citrix DaaS
To set up a site aggregation in Citrix DaaS, run the Post to service script. This script links a primary site with a secondary site in Citrix DaaS. As a result, administrators can switch sites more easily when managing them through Full Configuration and monitor sites through a unified Monitor console.
The Post to service script links a site in the Citrix DaaS.
Post to service script
$headers = @{}
$headers.Add("Accept","application/json")
$headers.Add("Content-Type","application/json")
$headers.Add("Authorization","CWSAuth bearer=XXXXXXX")
$uri = "https://resourceprovider.apps.cloud.com/HubCustomerID/aggregation"
$body = @{SpokeCustomerId="SpokeCustomerID"}
$bodyjson = $body | ConvertTo-Json
$resp = Invoke-RestMethod -Method Put -Uri $uri -Headers $headers -Body $bodyjson -ContentType 'application/json'
Write-Host "Status Code: $($resp.RawContent)"
<!--NeedCopy-->
Prepare and run the Post to service script
Get a fresh bearer token to reflect the changes that the Post to Cloud script made in Citrix Cloud.
- Open the PowerShell ISE. (If the PowerShell ISE is already open, clear the ISE working pane.) Paste the Post to service script into the working pane.
- On line 4, replace
CWSAuth bearer=XXXXXXX1with yourCWSAuthvalue (for example,CWSAuth bearer=AbCdef123Ghik…). This value is a long hash that resembles a certificate key. - On line 6, replace
HubCustomerIDwith the customer ID of the primary site. - On line 9, replace
SpokeCustomerIDwith the customer ID of the secondary site. - Run the script.
Remove an aggregation from Citrix DaaS
The Delete from service script removes an aggregation from Citrix DaaS.
Delete from service script
$headers = @{}
$headers.Add("Accept","application/json")
$headers.Add("Content-Type","application/json")
$headers.Add("Authorization","CWSAuth bearer=XXXXXXX")
$uri = "https://resourceprovider.apps.cloud.com/HubCustomerID/aggregation"
$body = @{SpokeCustomerId="SpokeCustomerID"}
$bodyjson = $body | ConvertTo-Json
$resp = Invoke-WebRequest -Method Delete -Uri $uri -Headers $headers -Body $bodyjson -ContentType 'application/json'
Write-Host "Response: $($resp.RawContent)"
<!--NeedCopy-->
Prepare and run the Delete from service script
- Open the PowerShell ISE and paste the Delete from service script into the working pane.
- On line 4, replace
CWSAuth bearer=XXXXXXX1with yourCWSAuthvalue (for example,CWSAuth bearer=AbCdef123Ghik…). This value is a long hash that resembles a certificate key. - On line 6, replace
HubCustomerIDwith the customer ID of the primary site. - On line 8, replace
SpokeCustomerIDwith the customer ID of the secondary site. - Run the script.
Remove an aggregation from Citrix Cloud
The Delete from Citrix Cloud script removes an aggregation from Citrix Cloud.
Delete from Citrix Cloud script
$headers = @{}
$headers.Add("Accept","application/json")
$headers.Add("Content-Type","application/json")
$headers.Add("Authorization","CWSAuth bearer=XXXXXXX")
$uri = "https://trust.citrixworkspacesapi.net/HubCustomerID/links/SpokeCustomerID"
$resp = Invoke-WebRequest -Method Delete -Uri $uri -Headers $headers
Write-Host "Response: $($resp.RawContent)"
<!--NeedCopy-->
Prepare and run the Delete from Citrix Cloud script
- Open the PowerShell ISE. (If the PowerShell ISE is already open, clear the working pane.) Paste the Delete from Citrix Cloud script into the working pane.
- On line 4, replace
CWSAuth bearer=XXXXXXX1with yourCWSAuthvalue (for example,CWSAuth bearer=AbCdef123Ghik…). This value is a long hash that resembles a certificate key. - On line 6, replace
HubCustomerIDwith the customer ID of the primary site. - On line 6, replace
SpokeCustomerIDwith the customer ID of the secondary site. - Run the script.
After the Delete from Citrix Cloud script completes, run the Get script to validate that the aggregation was removed.