Browser content redirection
Overview
The Linux VDA supports browser content redirection in Google Chrome. Browser content redirection provides the ability of rendering webpages in the allow list on the client side. This feature uses Citrix Workspace™ app to instantiate a corresponding rendering engine on the client side, which fetches the HTTP and HTTPS content from the URL.
Note:
You can specify which webpages are redirected to the client side by using an allow list. Conversely, you can specify which webpages are not redirected to the client side by using a block list.
This overlay web layout engine runs on the client instead of on the VDA and uses the client CPU, GPU, RAM, and network.
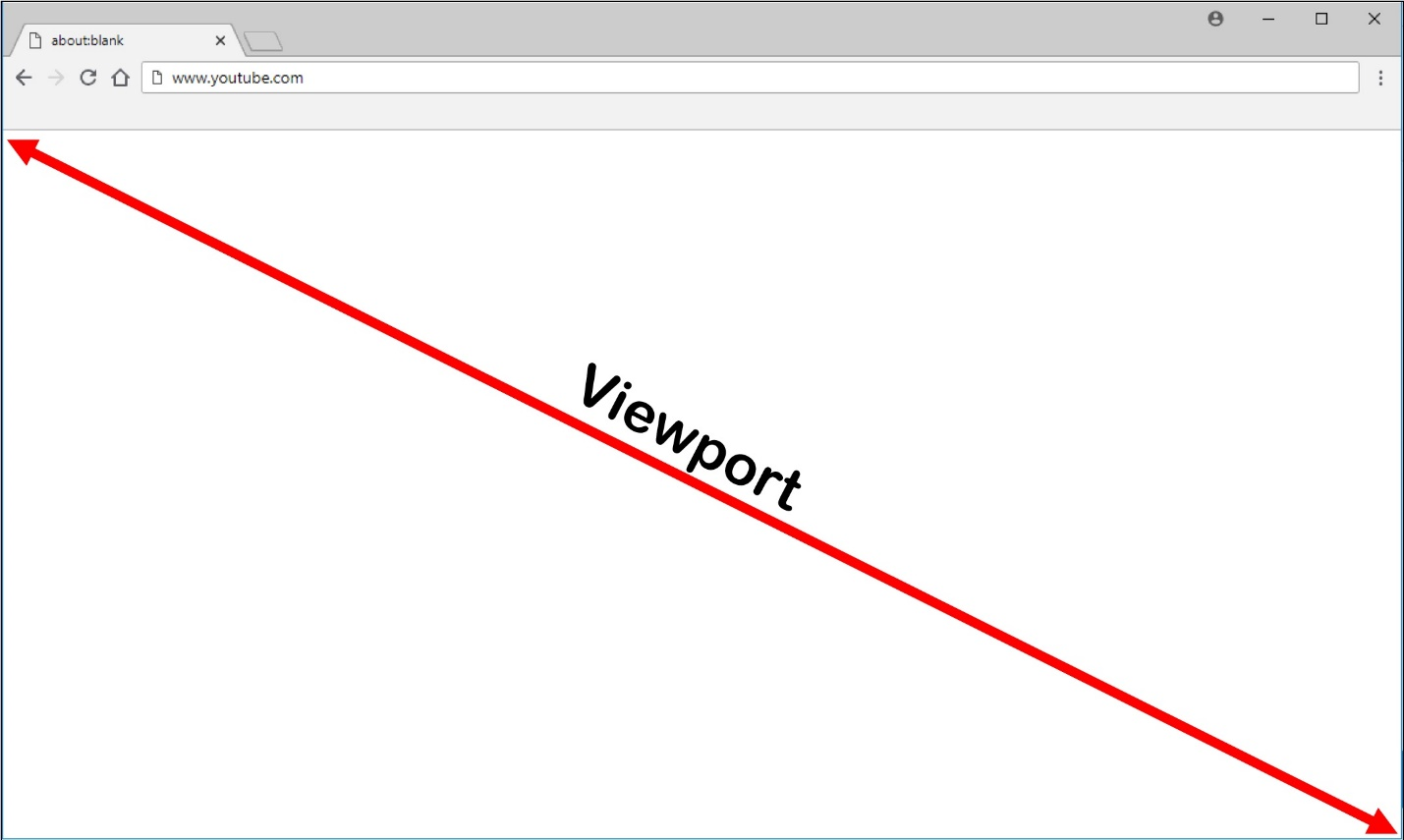
Only the browser viewport is redirected. The viewport is the rectangular area in your browser where content displays. The viewport does not include items such as the address bar, favorites bar, and status bar. Those items are still running in the browser on the VDA.
System requirements
Windows client:
- Citrix Workspace app 1809 for Windows or later
Linux VDA:
- VDA operating system: Ubuntu 20.04, Ubuntu 18.04, RHEL 7.8, RHEL 8.2, RHEL 8.1, SLES 12.5
- Browser on the VDA: Google Chrome v66 or later with the Citrix® browser content redirection extension added
Configure browser content redirection
-
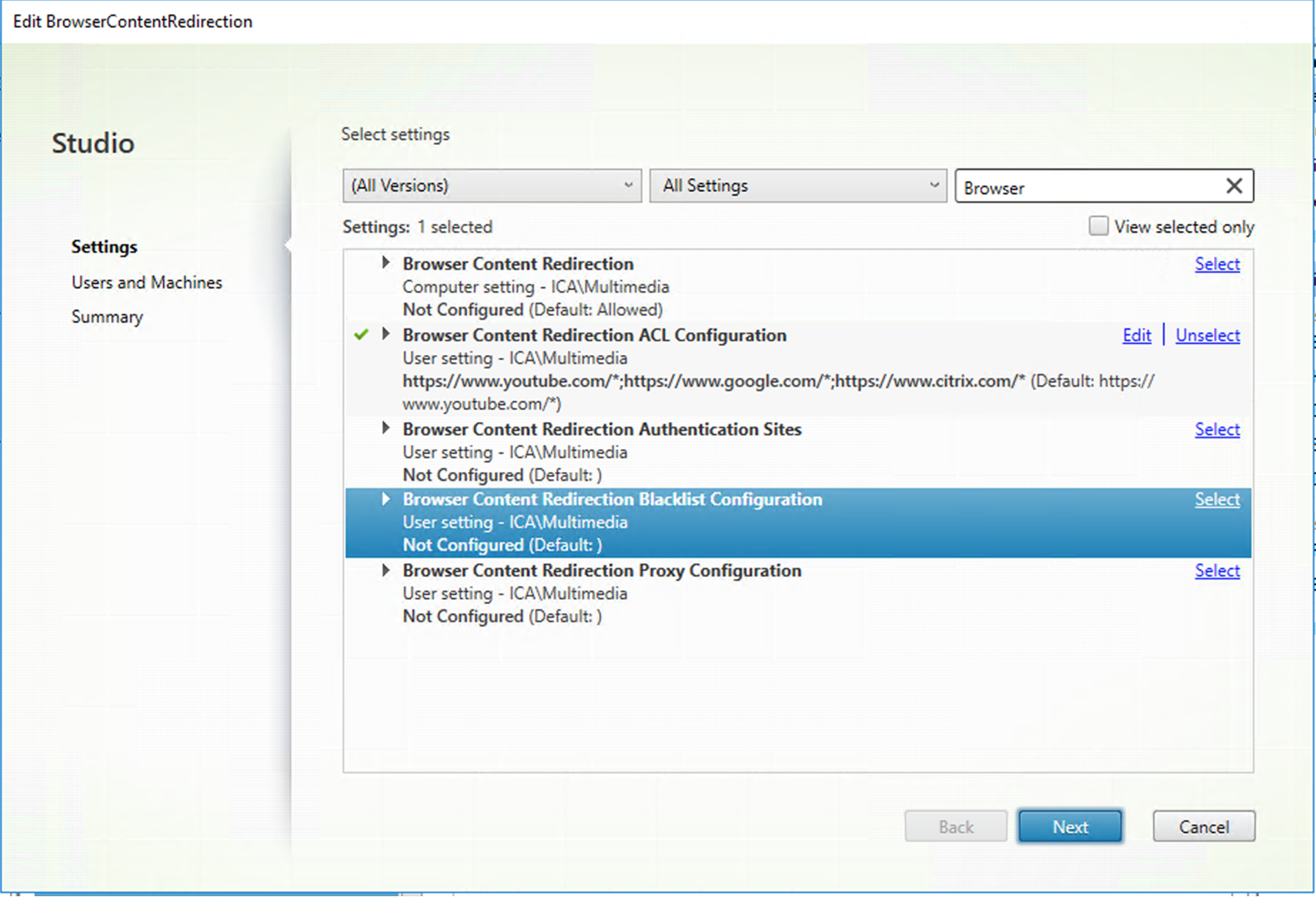
In Citrix Studio, configure policies to specify an allow list and a block list of URLs for browser content redirection. Browser content redirection is set to Allowed by default.
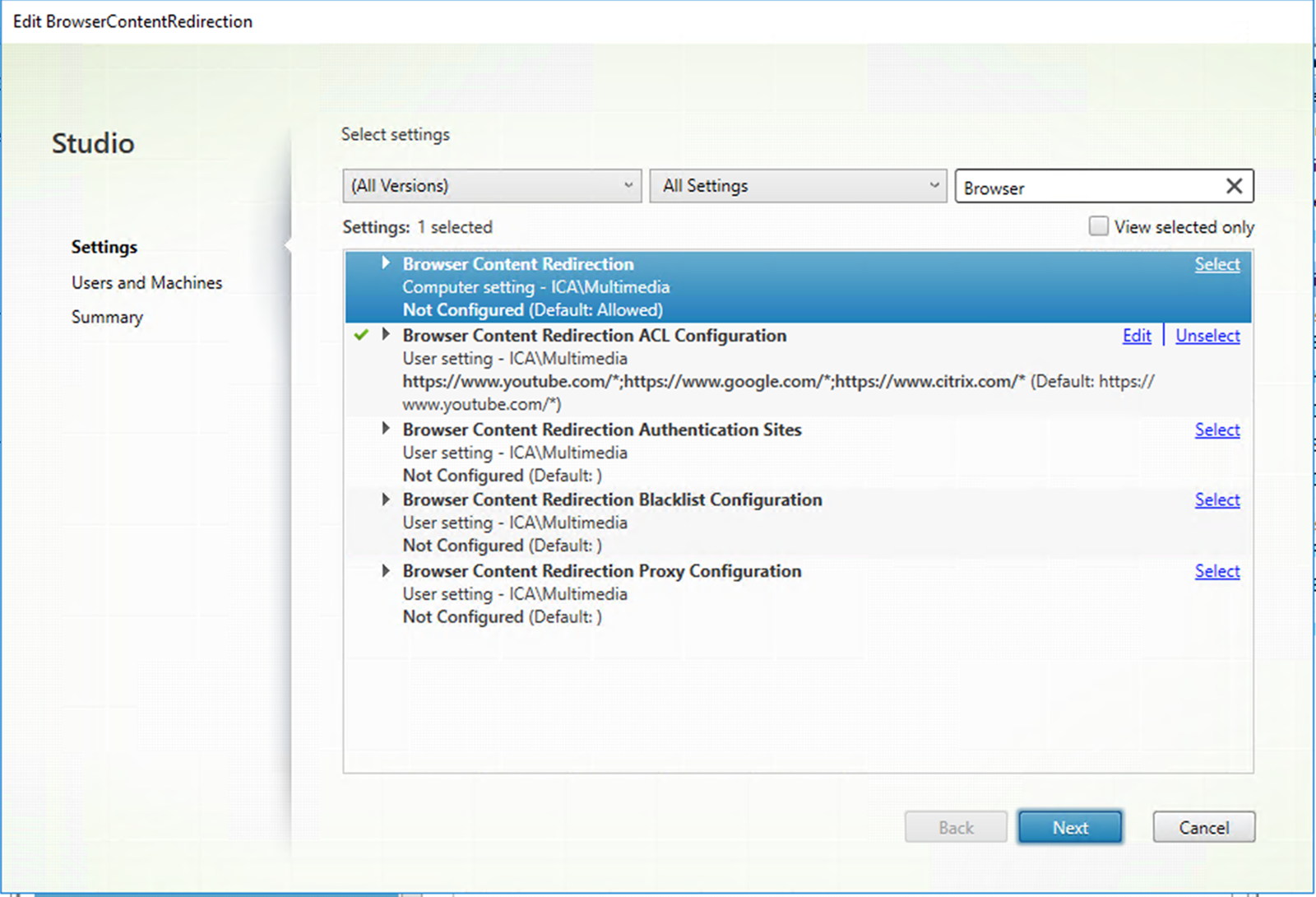
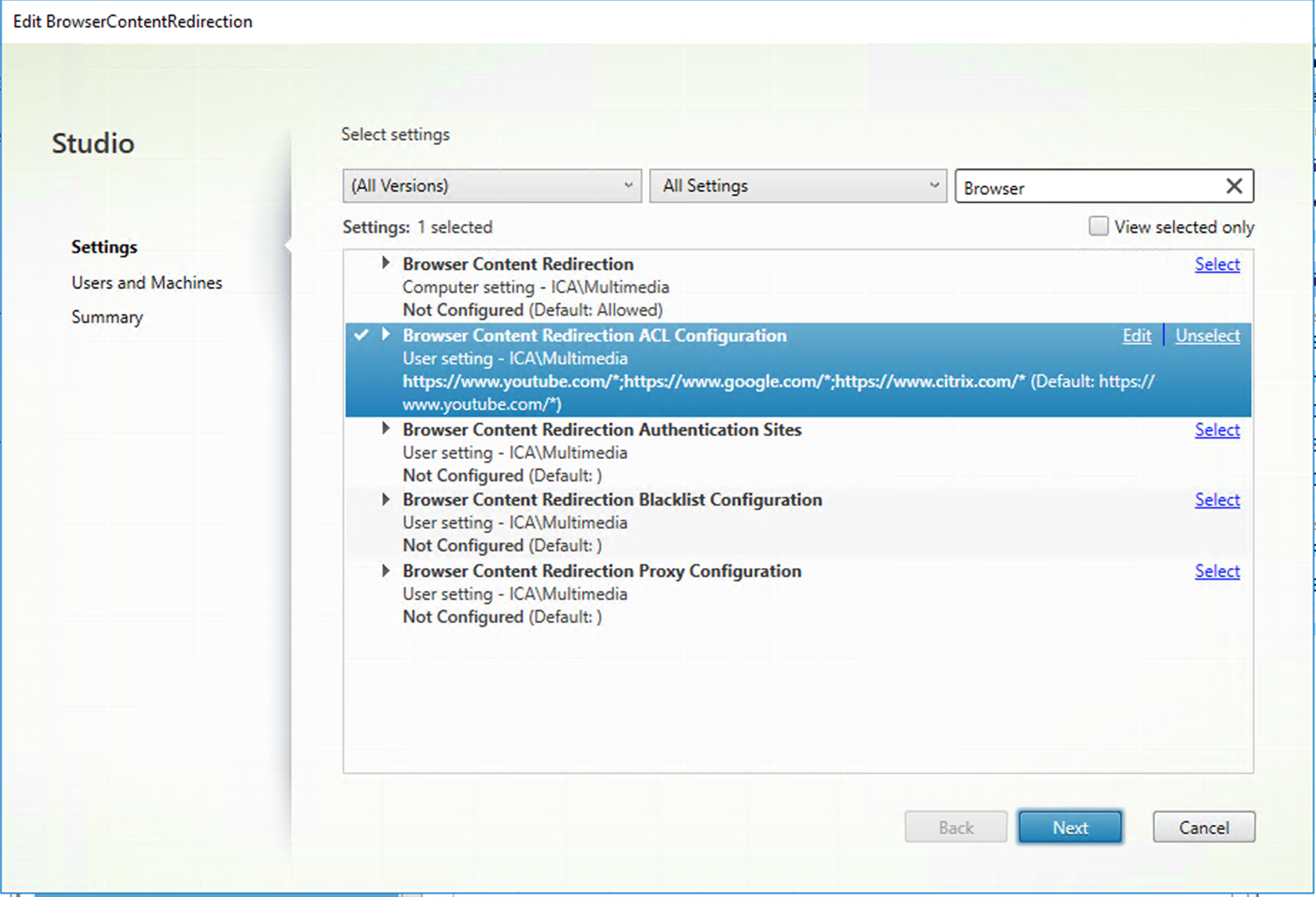
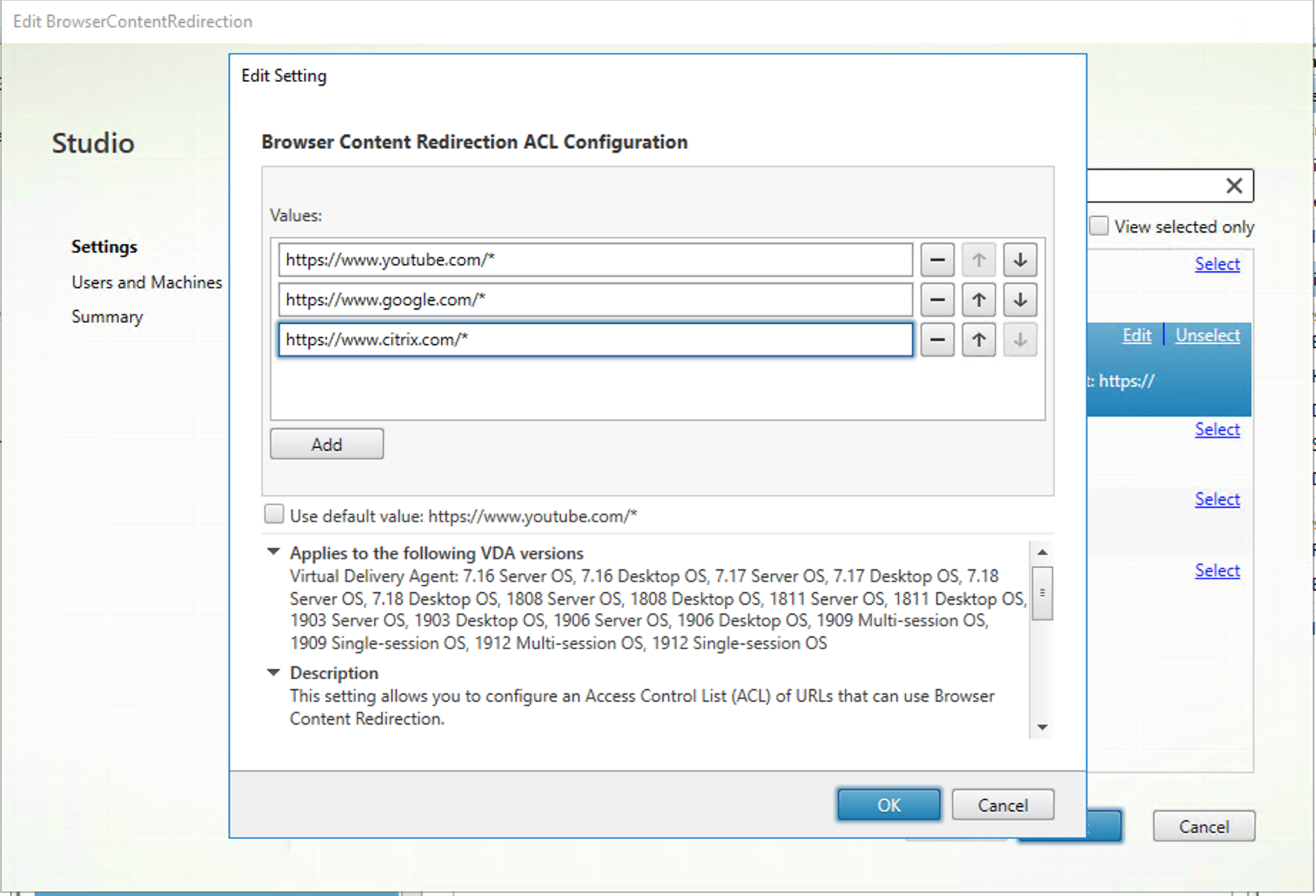
The Browser Content Redirection ACL Configuration setting specifies an allow list of URLs that can use browser content redirection.
The Browser Content Redirection Blacklist Configuration setting specifies a block list of URLs that cannot use browser content redirection.
Note:
The Linux VDA currently does not support the Browser Content Redirection Proxy Configuration setting.
-
Click Add to Chrome on the VDA to add the Citrix browser content redirection extension from the Chrome Web Store. Doing so helps the browser on the VDA to detect whether a URL (being navigated to) matches an allow list or a block list.
Important:
The extension is not required on the client. Add it only on the VDA.
Chrome extensions are installed on a per-user basis. Updating a golden image to add or remove an extension is not required.
If a match to a URL is found in an allow list (for example, https://www.mycompany.com/) but not in any block list, a virtual channel (CTXCSB) instructs the Citrix Workspace app that a redirection is required and relays the URL. Citrix Workspace app then instantiates a local rendering engine and displays the website.
Citrix Workspace app then blends back the website into the virtual desktop browser content area seamlessly.
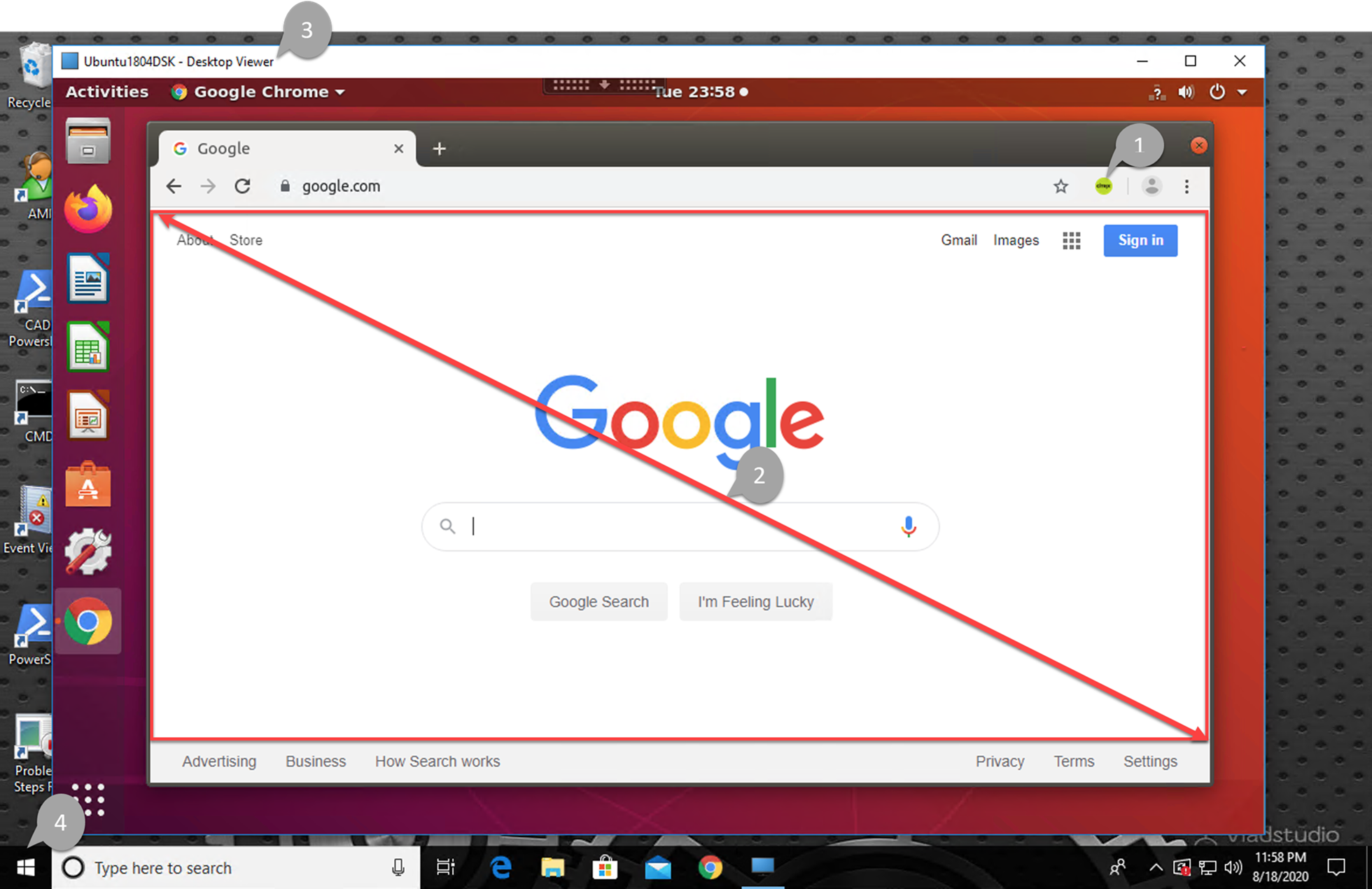
-
Icon of the Citrix browser content redirection extension
The color of the extension icon specifies the status of the Chrome extension. It is one of the three colors:
- Green: Active and connected
- Gray: Not active/idle on the current tab
- Red: Broken/Not working
- Viewport rendered on the client or blended back to the virtual desktop
- Linux VDA
- Windows client
Redirection scenarios
Here are scenarios of how the Citrix Workspace app fetches content:
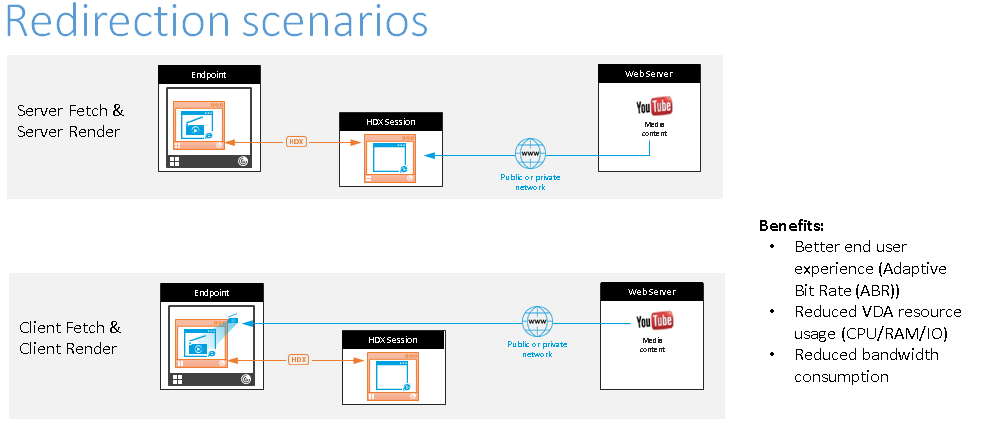
- Server fetch and server render: There is no redirection because you did not add the site to the allow list or the redirection failed. We fall back to rendering the webpage on the VDA and use Thinwire to remote the graphics. Use policies to control the fallback behavior. This scenario causes high CPU, RAM, and bandwidth consumption on the VDA.
- Client fetch and client render: Because the Citrix Workspace app contacts the web server directly, it requires Internet access. This scenario offloads all the network, CPU, and RAM usage from your Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops™ site.
Fallback mechanism
There might be times when client redirection fails. For example, if the client machine does not have direct Internet access, an error response might go back to the VDA. In such cases, the browser on the VDA can then reload and render the page on the server.